CS224N|Lecture 4 Backpropagation and Computation Graphs
10 Aug 2021
word vector 자체를 학습시키는 것의 문제점과 그에 대한 해결책, back propagation할때 실제 그 내부에서 어떤일이 일어나는지에 대한 내용 이었다. 그리고 modern framework인 pytorch, tensorflow 등에는 Automatic Differentiation이 적용되어 자동으로 계산이 이뤄진다는 것을 배웠다. 마지막으로 grab of bag of miscellaneous stuff라고 교수님이 말한 학습시 고려해야 할 여러가지를 수업했다. 대부분 아는내용이 었지만, symbolic computation을 통한 automatic differentiation은 처음 배웠다.
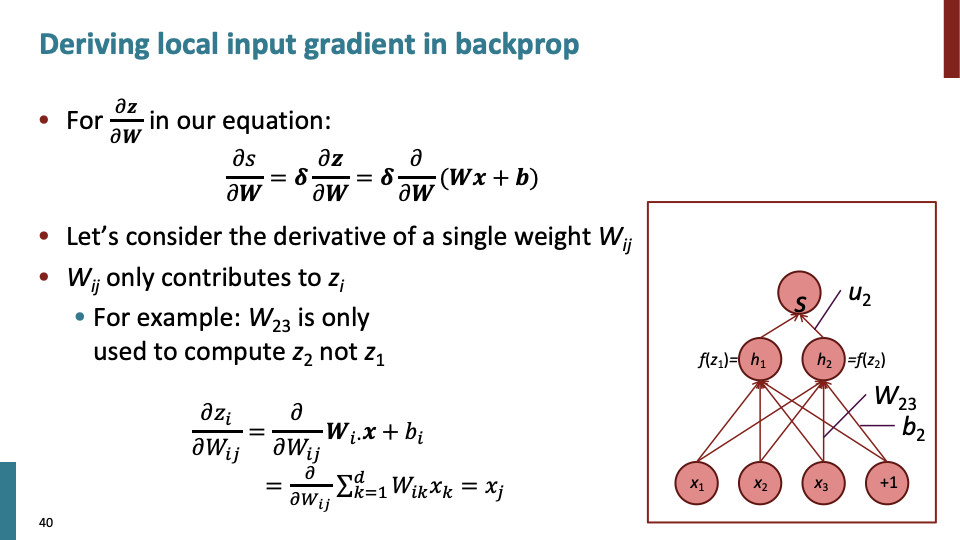
수업에서 $\delta$를 error signal라고 불렀고, back propagation시에, upstream(위에서부터) 내려오는 값이고, 이 값을 이용하여 gradient를 효율적으로 빠르게 계산한다.
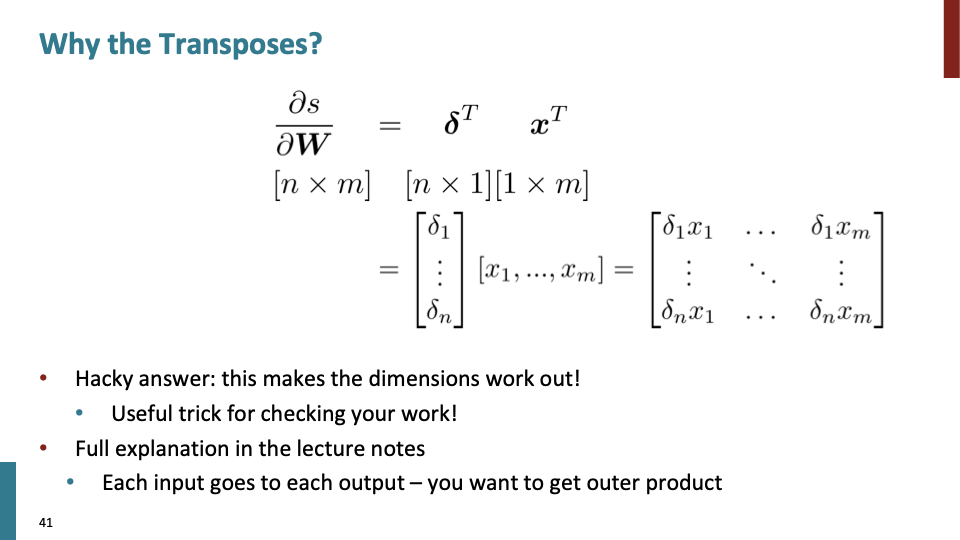
Transpose하는 이유는 dimension을 유지하기 위해 하는것이다. derivatives(미분)한 행렬의 shape도 shape convention을 따르도록 해야 한다.
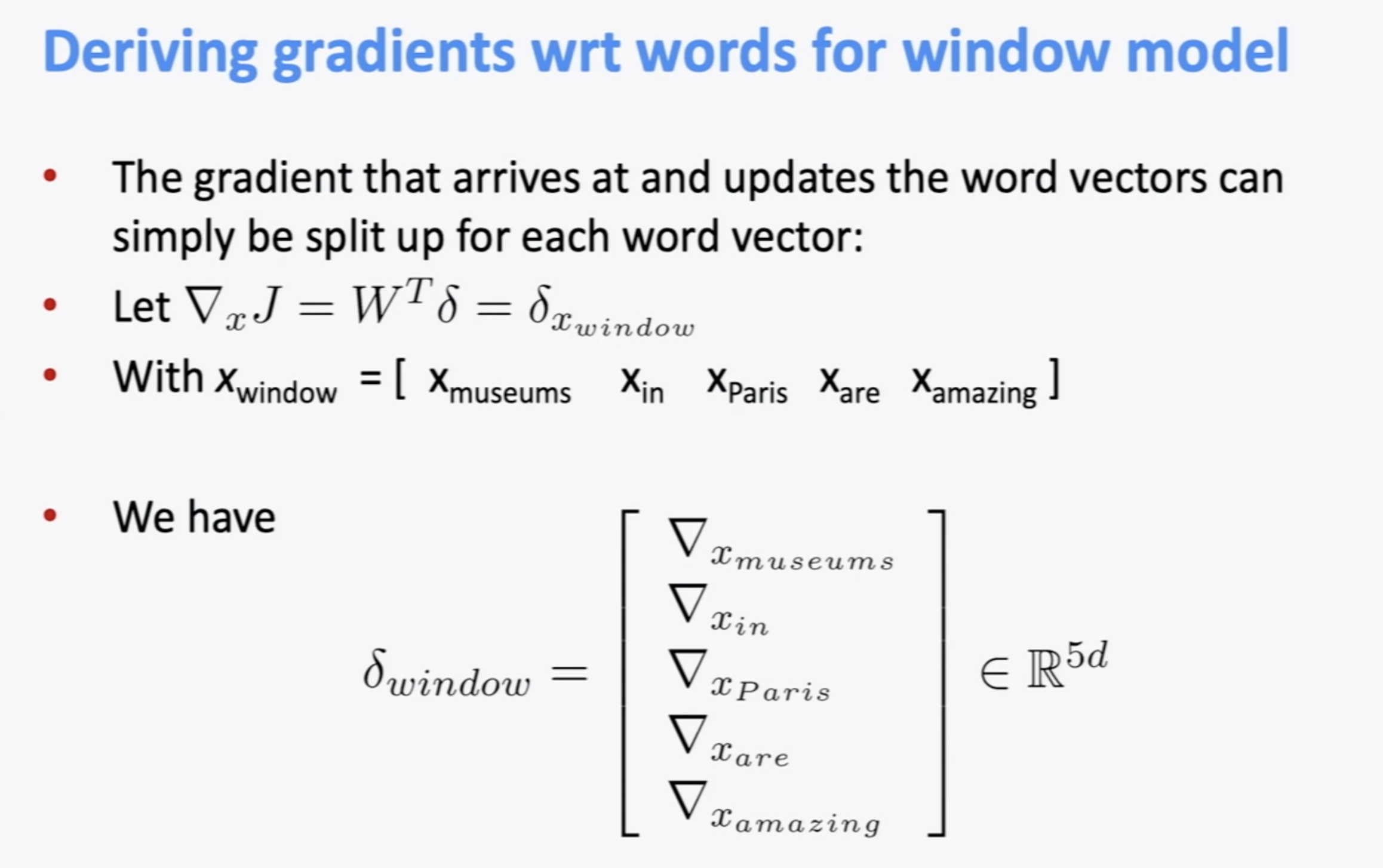
word vector에 대해 학습을 하면 window size가 5일 경우 delta는 5-d dimension이 된다. 그런데 데이터의 크기에 따라 문제가 생긴다.
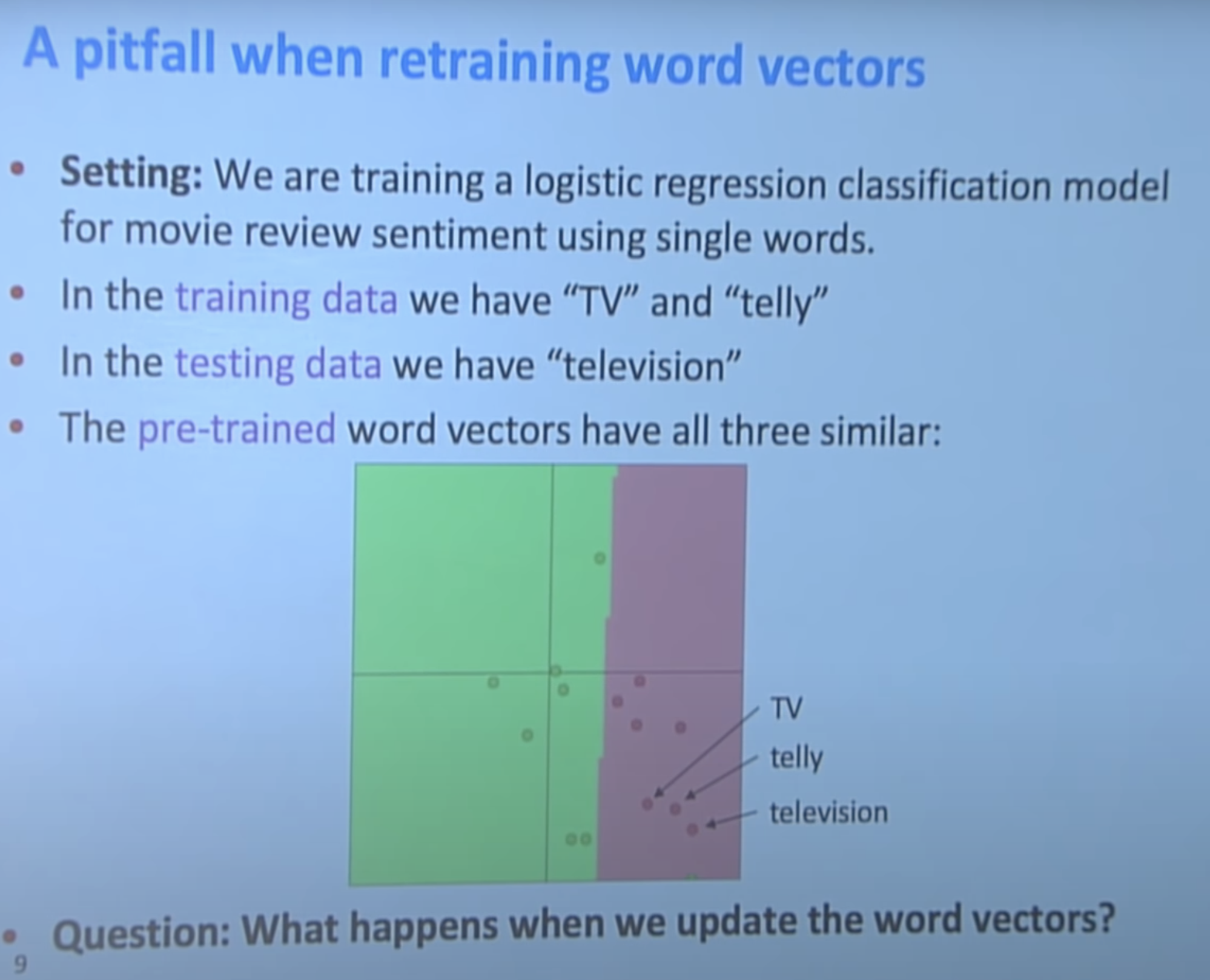
TV, telly, television 3개의 단어는 기본적으로 같은 뜻이기 때문에 word vector space상에서 매우 가깝게 위치해야한다. 하지만 training data에 TV, telly만 있는 경우, classifier는 television이 같은 의미인지 모른다.
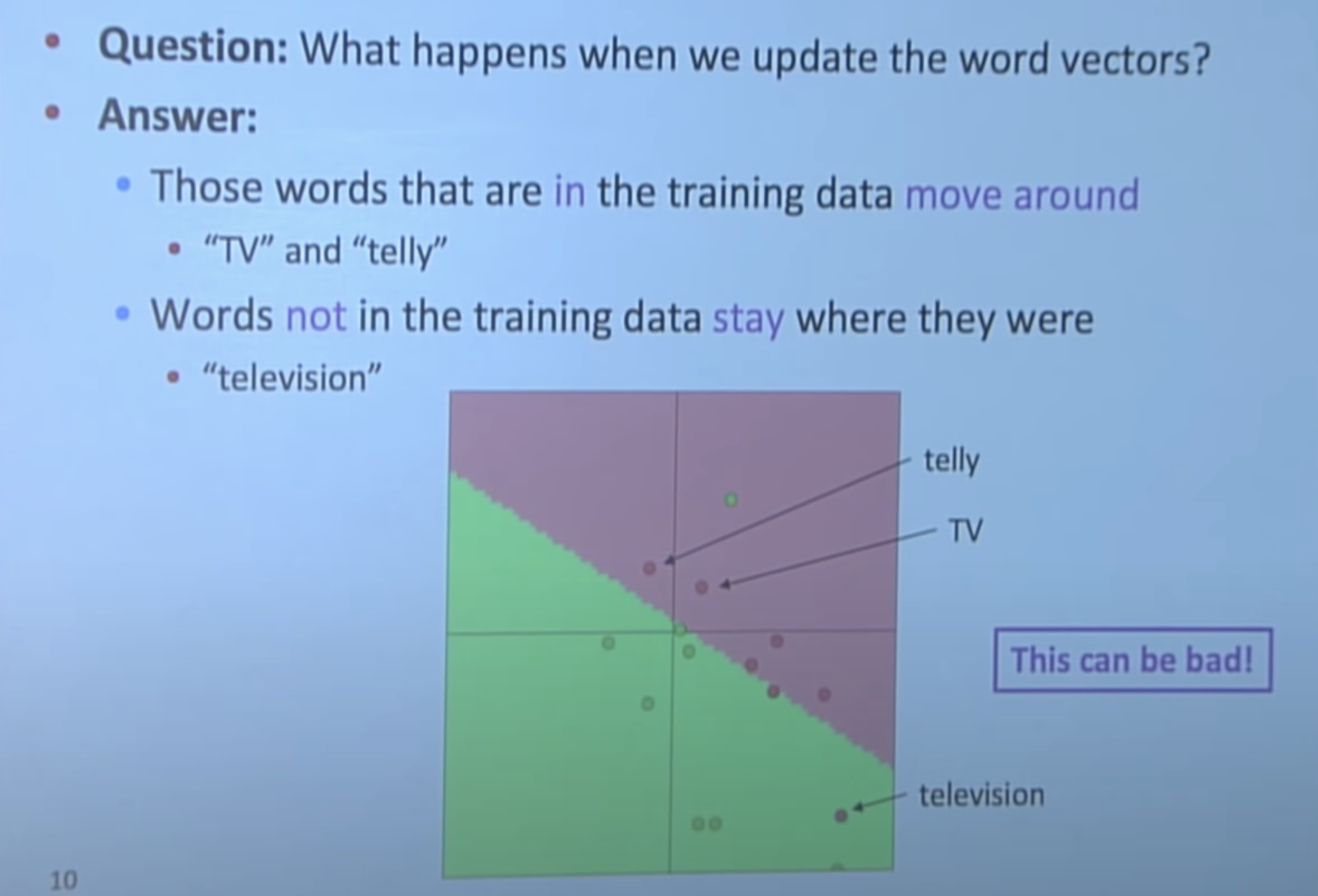
그래서 다음과 같이 classifier가 형성된다.
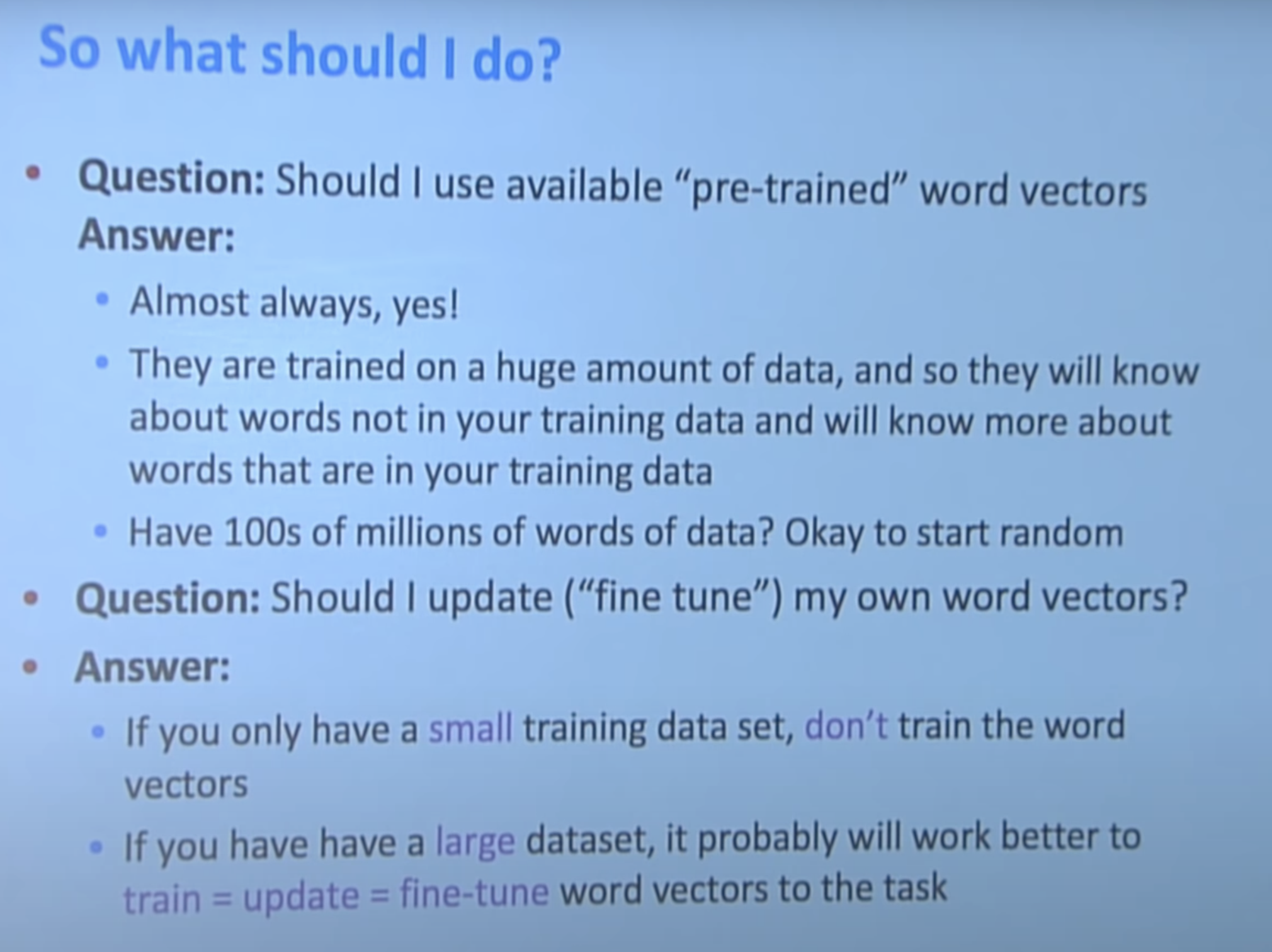
그래서 대부분의 경우 pre-trainded된 word vector를 사용해야한다. 하지만 만약 100M이상의 words of data가 있다면 word vector에 대해 학습해도 된다. 사실 현업에서는 둘다 해보고 수치가 좋은것을 선택한다고 한다.
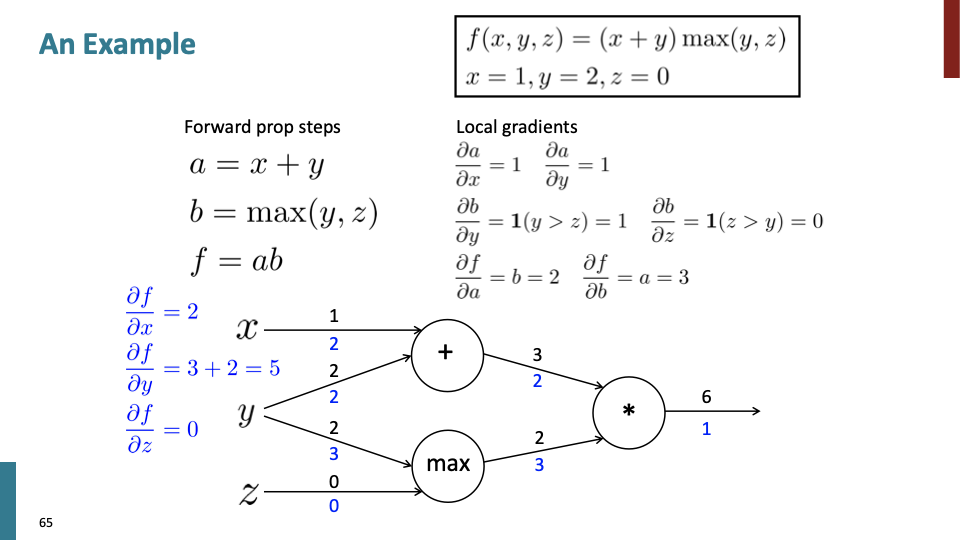
’+’, ‘max’, ‘*‘가 노드에 있을때 back propagation하는 수식을 나타낸것이다.
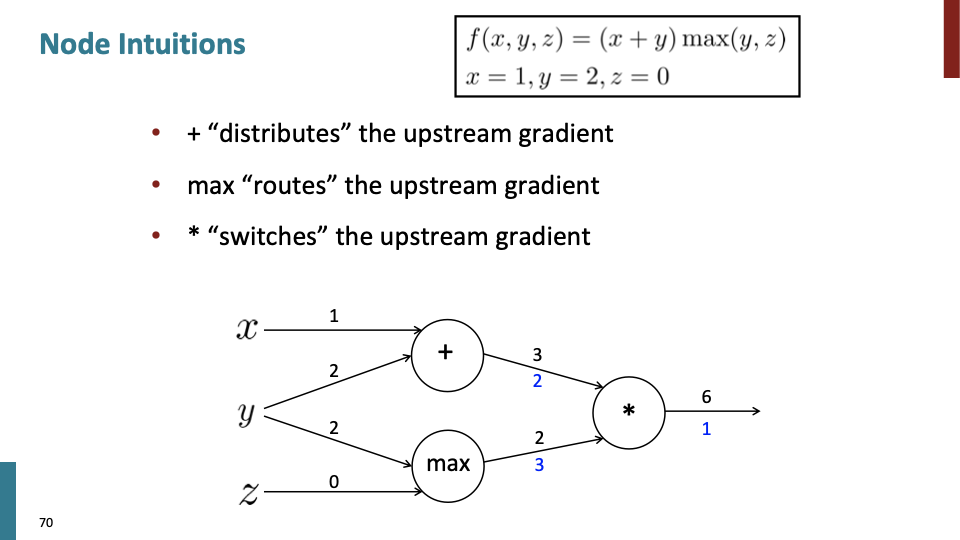
이전 슬라이드에서 볼수 있듯이, ‘+’ 노드는 “distribute”하고, ‘max’ 노드는 “route”하고, ‘*’ 노드는 “switch”한다.
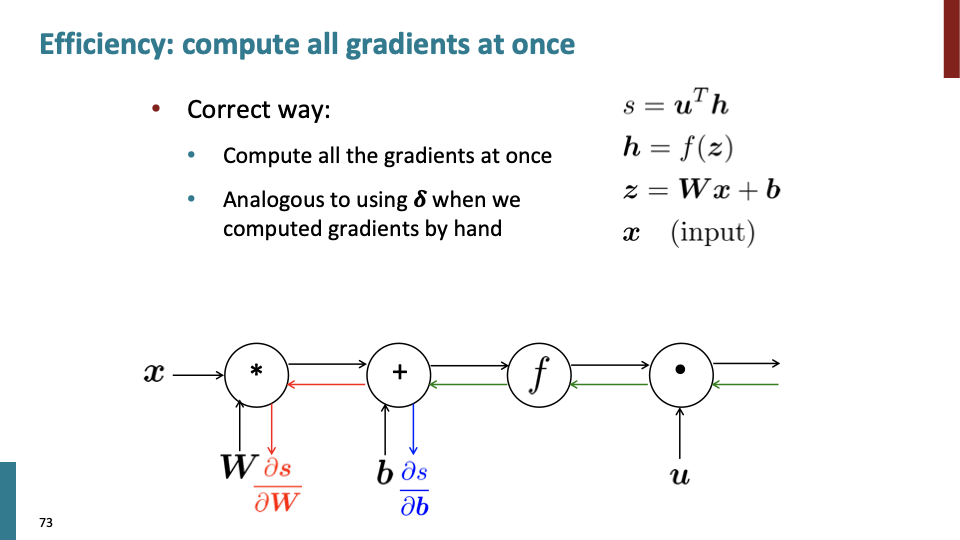
back propagation 계산할때, 위에서 아래로 하나씩 하는게 아니라 모든 gradient를 한꺼번에 계산한다. error signal이라고 하는 $\delta$에 대해 각 노드에서 계산을 해준후 update해야할 weight가 있는 노드에 와서 차례대로 계산한다. upstream에서 gradient를 계산할때, $\delta$이 shared variable이라고 볼 수 있다.
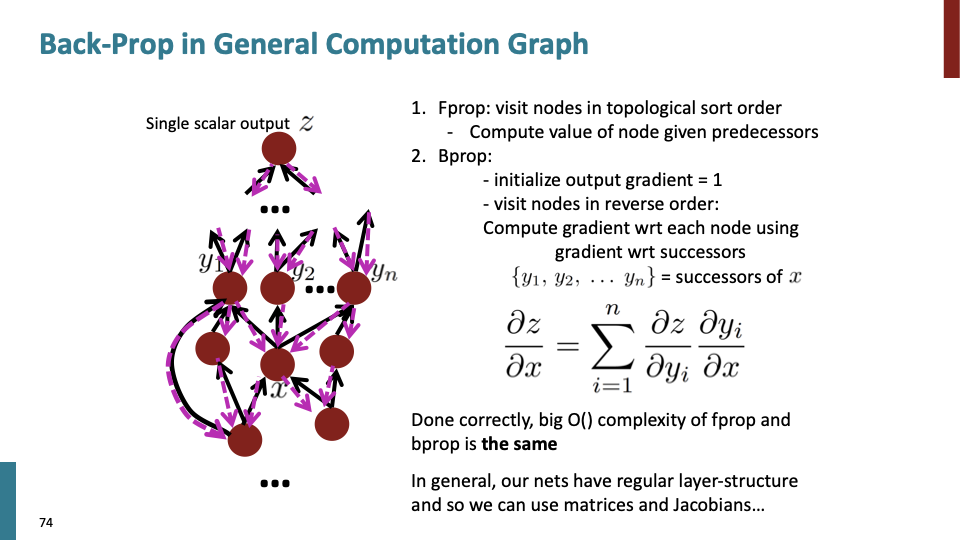
위상정렬(toplogical sort)을 통해 노드를 방문하며 forward propagation을 한다. 그 이후에 reverse order로 back propagation을 한다. 한번에 gradient를 계산하기 때문에 위상정렬하여 노드를 방문하는 시간복잡도가 fprop, bprop에 동일하게 적용된다.
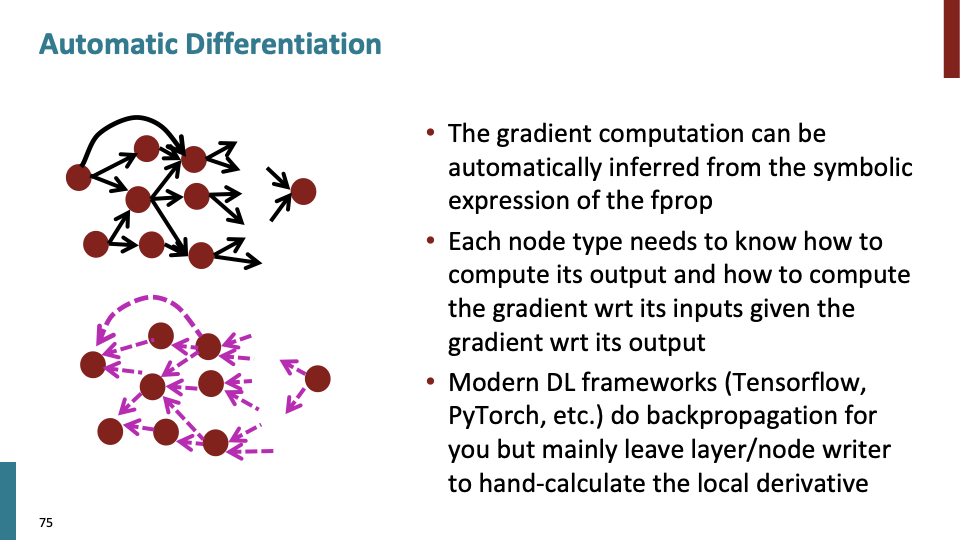
symbolic computation을 통해 구현된 automatic differentiation은 modern DL framework인 tensorflow와 pytorch 등에 구현되어있다. symobolic computation에 대해서는 따로 공부하여 포스트를 올릴 예정이다.
아래는 back prop 구현에 대한 간단한 코드이다.
class ComputationalGraph(object):
#...
def forward(inputs):
# 1. pass inputs to input gates
# 2. forward the computational graph:
for gate in self.graph.nodes_topologically_sorted():
gate.forward()
return loss # the final gate in the graph outputs the loss
def backward(self):
for gate in reversed(self.graph.nodes_topologically_sorted()):
gate.backward() # little piece of backprop (chain rule applied)
return inputs_gradients
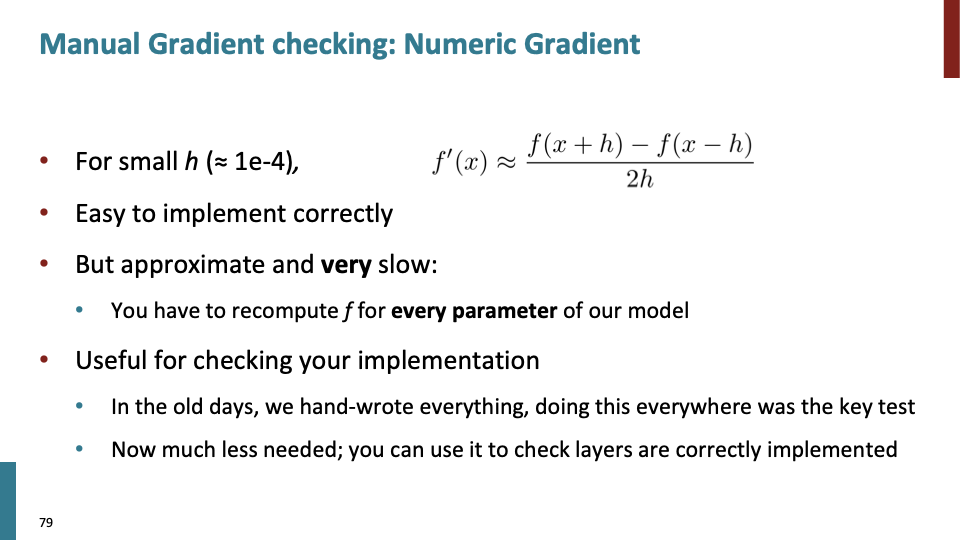
2014년대 초기 까지는 gradient checking을 통해 Numeric gradient를 모든 check했지만 요즘은 필요하지 않다.
gradient를 배워야하는 이유는 compiler를 배워야하는 이유와 비슷하다고 했다. Karpthy article도 한번 봐야 겠다.
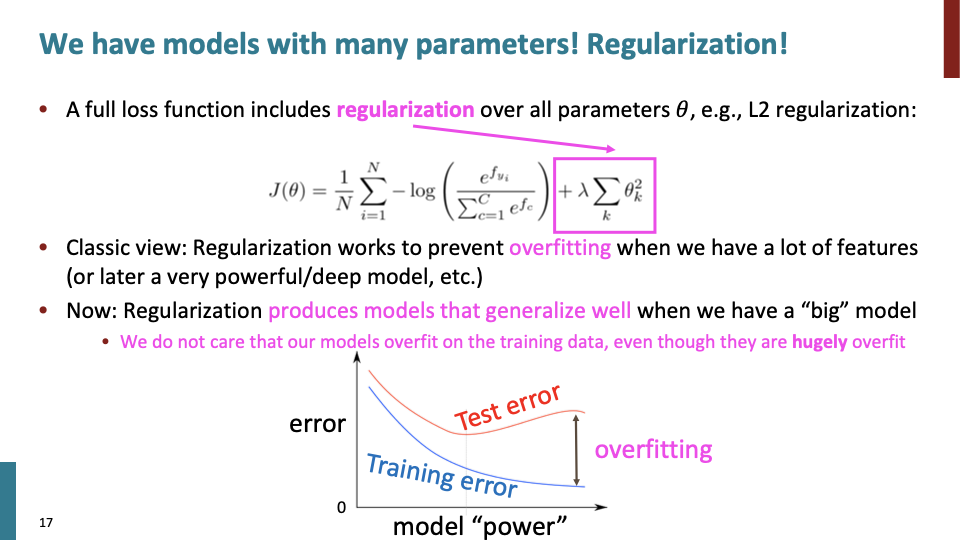
이제 여기서부터 교수의 표현으로 잡다한(?) 여러가지 내용이다. reularization을 통해 overfitting을 방지한다. overfitting이 일어나는 이유는 unseen data에 대해 model이 generalize되지않아 일어나는 것이다. 가령 위에서 word vector를 학습시켰을때 일어나는 문제도 포함된다.

단순히 vectorization 뿐만 아니라 matrixization 혹은 더 높은 차원에 대한 tensorization은 Deep lerarning system이 빠르고 효율적으로 계산하게 해준다. 위의 코드에서 vectorization않은 코드는 for를 계속 돌며 하나씩 계산해야 되서 느리다. numpy의 연산속도가 빠른 이유도 유사하다. (예전에 면접에서 답하지 못한 질문 중 하나.. 정리해서 글 올릴 예정이다.)
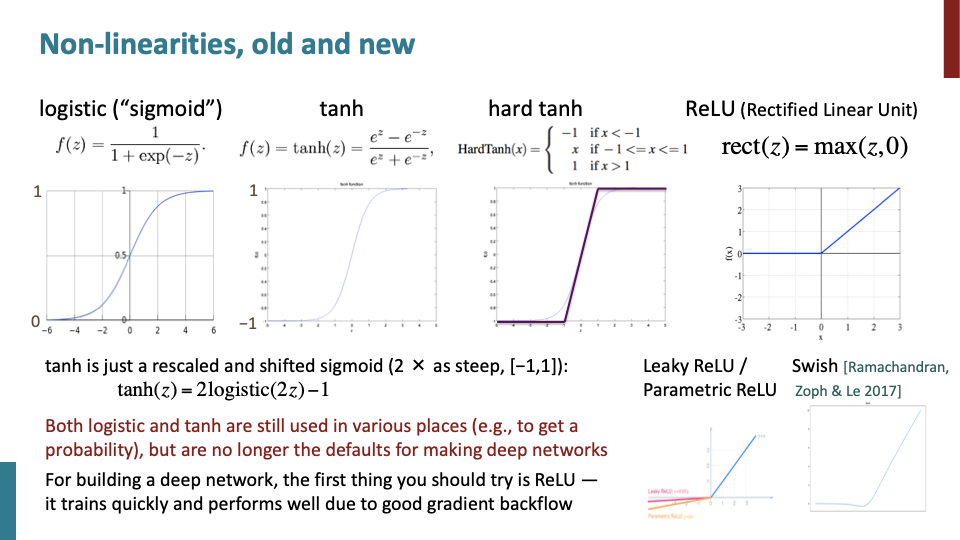
sigmoid는 80s~90s early neural net에 많이 사용됬었지만, 요즘에는 output을 1 or 0으로 출력하는 일이 아니라면 쓰이지 안쓴다. tanh는 사실 rescaled, shifted version of sigmoid이다. 그리고 tanh(z)안에 있는 exponential의 연산이 느려서 사람들이 빠르게 계산하기 위해 hard tanh를 만들었고, 이것은 꽤 많이 사용한다. ReLU는 default choice로 back prop계산이 매우 빠르다.
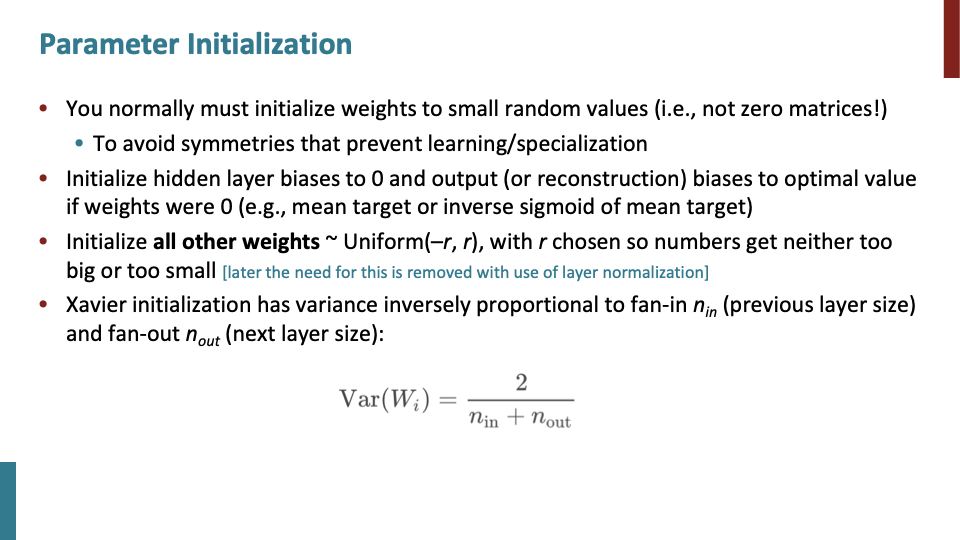 weight값을 0으로 시작하면 symmetry하게 학습되는 문제가 생길 수 있다. 그래서 small random value로 시작하는 것이 좋다. Xavier initialization이 보통 선택하는 initialization이다.
weight값을 0으로 시작하면 symmetry하게 학습되는 문제가 생길 수 있다. 그래서 small random value로 시작하는 것이 좋다. Xavier initialization이 보통 선택하는 initialization이다.

보통 complex net들을 위해 누적된 gradient에 의해 parameter들이 수정되는 family of adapative optimizer를 선택한다. 그리고 꽤 잘 작동한다.

learning rate에 관한 내용이다.

마지막으로 drop out에 관한 내용이다.