최소 스패닝 트리(MST:Minimum Spanning Tree)
07 Aug 2021
CTP 알고리즘 동아리에서 여름방학 코딩테스트반에 참여하여 공부한 내용입니다.
아래 자료는 수업에서 사용한 내용입니다.
MST란?
- 최소 스패닝 트리(=최소 신장 트리)
-
스패닝 트리
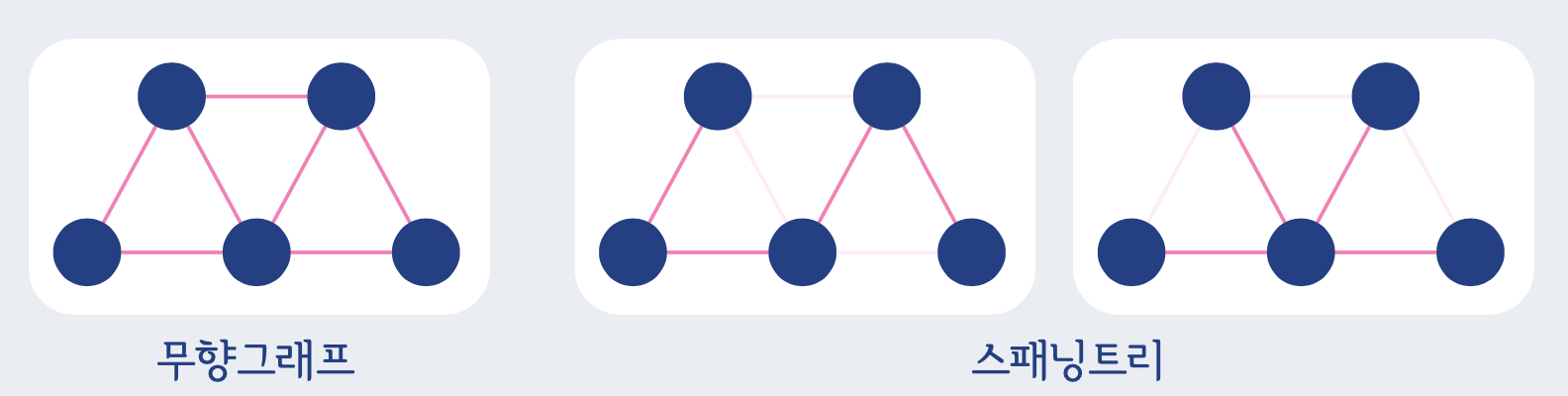
- 무향그래프 G의 스패닝 트리 T : G의 모든 정점을 포함하는 트리인 부분 그래프
- 한 그래프에 여러 스패닝 트리가 존재할 수 있다.
- 스패닝 트리 역시 트리이므로, 트리의 성질을 갖는다.
- 간선의 수 = 정점의 수 -1
- 사이클이 존재하지 않음
-
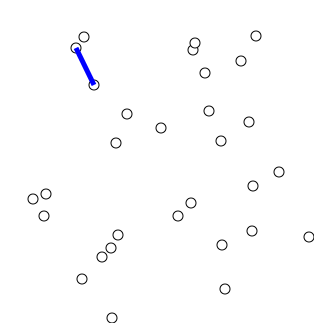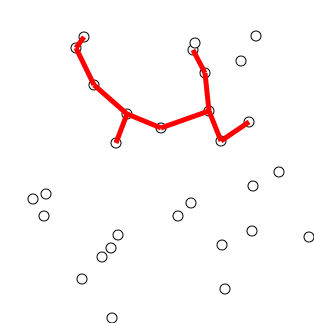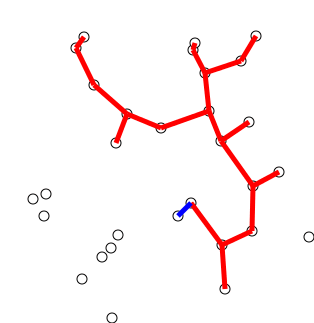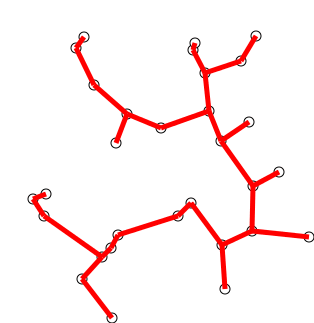
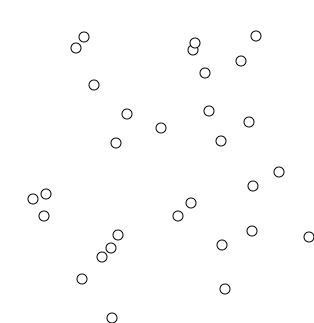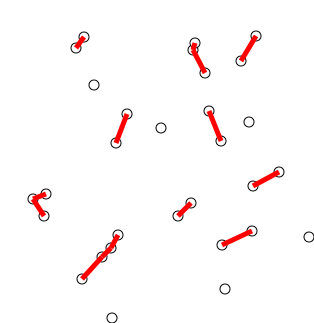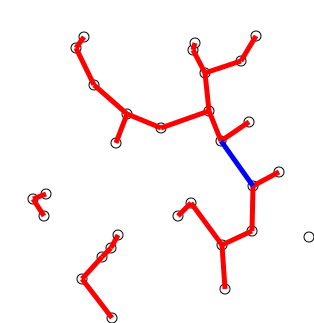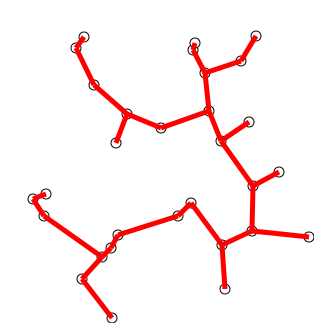
최소 스패닝 트리
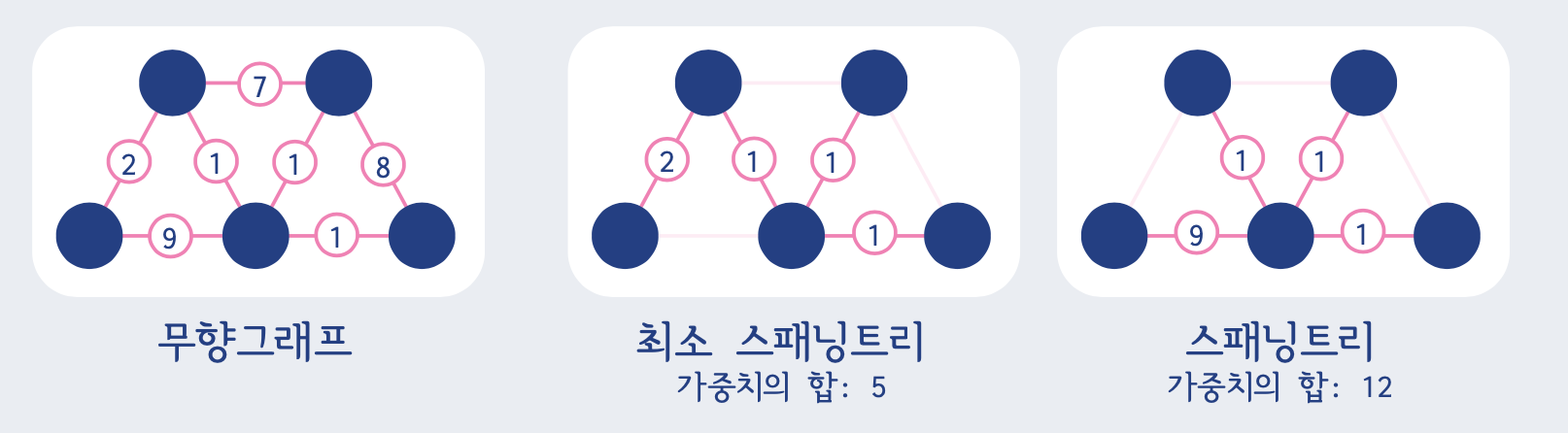
- 간선에 가중치가 있는 무향 그래프의 스패닝 트리 중 가중치의 합이 최소 인 것
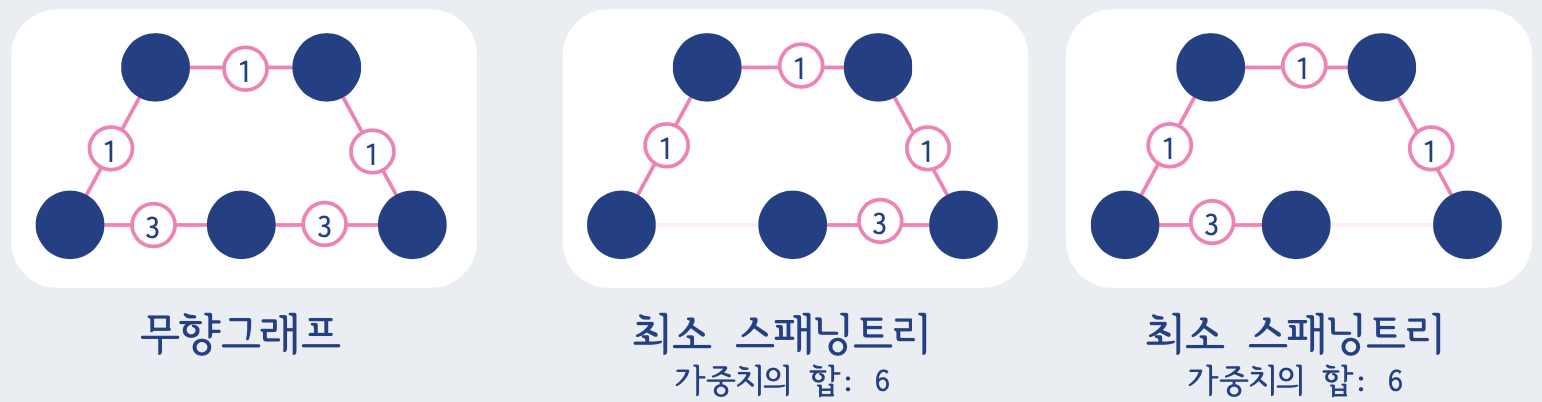
- 한 그래프에 여러 최소 스패닝 트리가 존재할 수 있다.
프림 알고리즘 (Prim Algorithm)
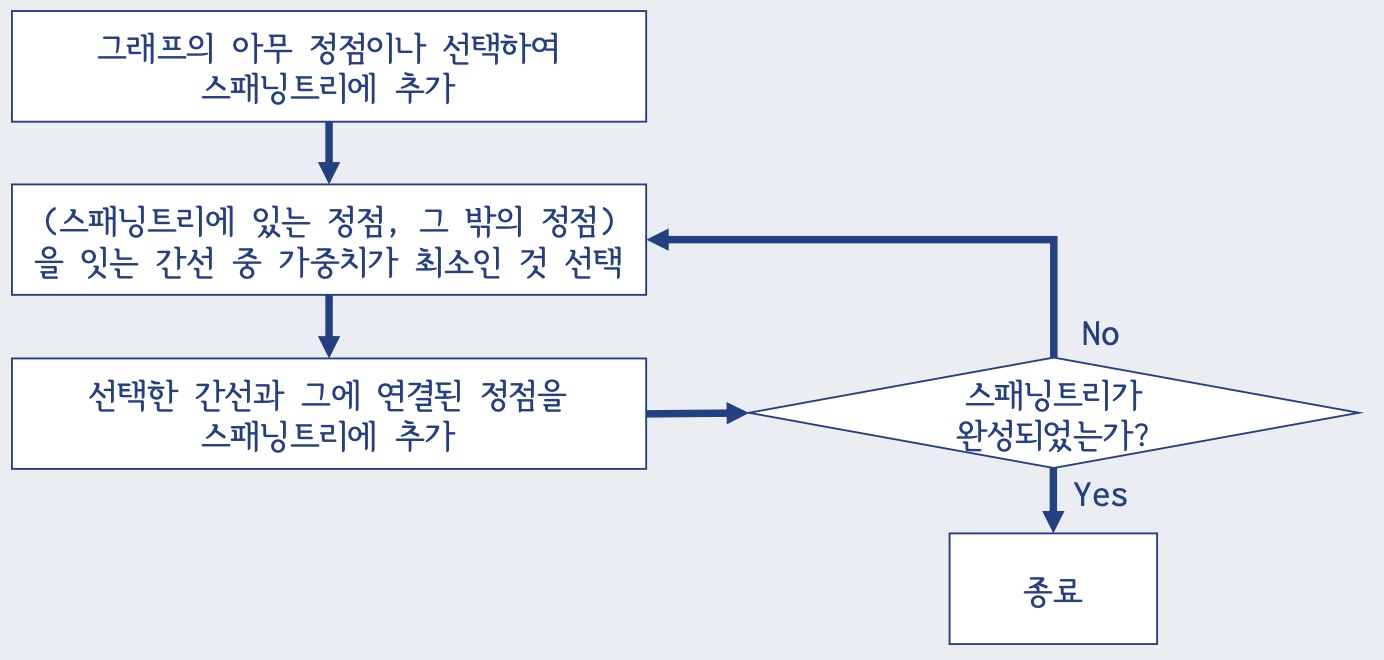
프림 알고리즘 : 구현
- O(N^2), O(E*logN) 등 다양한 구현방법이 존재한다.
- O(E*logN))
- 스패닝트리에 가장 가까운 간선을 O(logN)에 구하기 위한 자료구조 활용 (set, 우선순위큐 등)
- (반복) 마지막으로 추가한 정점과 연결된 간선을 자료구조에 삽입 > 스패닝트리에 가장 가까운 정점 추가
크루스칼 알고리즘
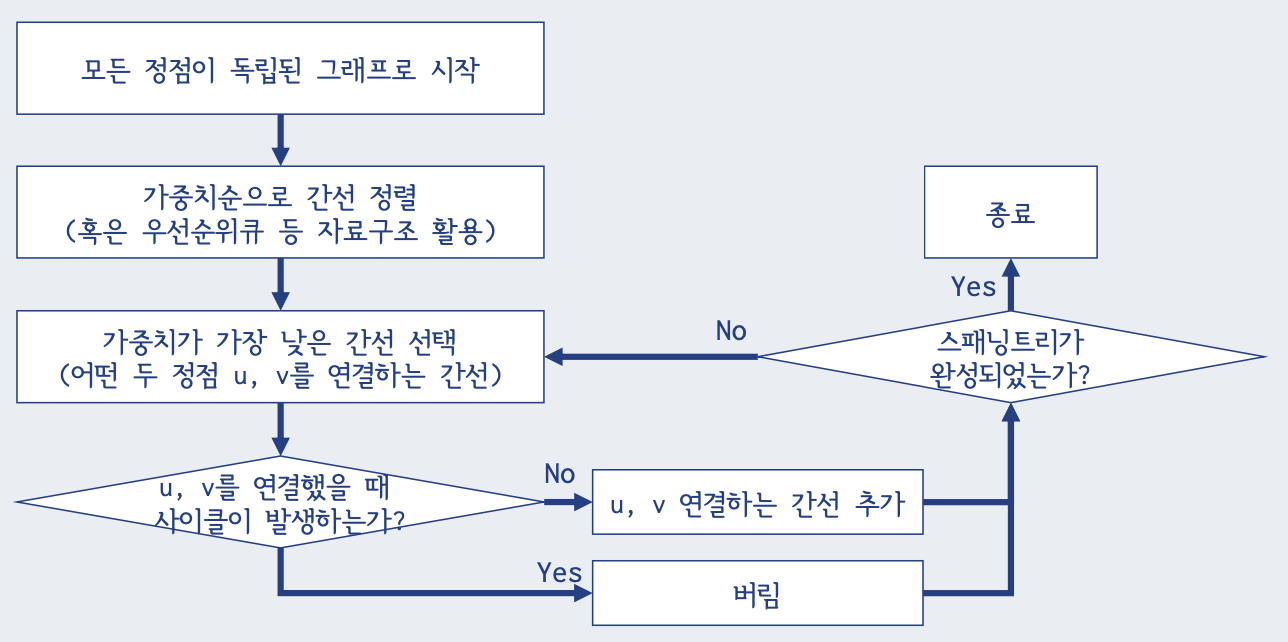
D - 최소 스패닝 트리
DSU를 이용하여 O(E*logN)시간에 크루스칼 알고리즘을 구현할것이다.
code
#include <tuple>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
using tup = tuple<int,int,int>;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
priority_queue<tup,vector<tup>,greater<tup>> edge;
int v,e,ans=0;
int par[10010];
vector<vector<pi>> vv;
int find(int a) {
if (par[a] == a) return a;
return par[a] = find(par[a]);
}
void merge(int a, int b) {
int a_root = find(a), b_root = find(b);
if (a_root != b_root) par[a_root] = b_root;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>v>>e;
for(int i=1;i<=v;i++)par[i]=i;// 독립적인 그래프가 v개 생김.
for(int i=0;i<e;i++){
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
edge.push({c,a,b});
}
int edgeCnt = 0;
while(!edge.empty()){
int weight = get<0>(edge.top()),a=get<1>(edge.top()),b=get<2>(edge.top());
edge.pop();
// 같은 집합 -> 같은 component에 속한다고 했을때, 간선이 추가되면 사이클이 생긴다.
// 사이클이 존재하는지 여부는 두 정점에 대해 find 함수를 이용하여 같은 부모를 갖는지 확인하면 된다.
int root_a = find(a), root_b=find(b);
if(root_a==root_b) continue;
merge(a,b); // union
edgeCnt+=1;
ans += weight;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
E - 도시 분할 계획
MST로 주어진 도시들을 이어주는 최소 스패닝 트리를 만든 후에,가장 큰 가중치의 도로를 빼주면 2개의 도로로 분리가 된다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <tuple>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
using tup = tuple<int,int,int>;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
//priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
priority_queue<tup,vector<tup>,greater<tup>> edge;
int n,m;
int par[100001];
int find(int a){
if(a==par[a]) return a;
return par[a]=find(par[a]);
}
void merge(int a,int b){
int a_root = find(a),b_root=find(b);
if(a_root!=b_root) par[a_root]=b_root;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i;
for(int i=0,p1,p2,p3;i<m;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2>>p3;
edge.push({p3,p1,p2}); // 가중치를 우선순위큐에 넣어서 정렬해야함.
}
int ans =0;
int max_cost = 0;
while(!edge.empty()){
int a=get<1>(edge.top()),b=get<2>(edge.top()),c=get<0>(edge.top());
edge.pop();
int a_root = find(a);
int b_root = find(b);
if(a_root==b_root) continue;
merge(a,b);
ans+=c;
max_cost=max(c,max_cost);
}
cout<<ans-max_cost;
}
F - 창영이와 퇴근
다익스트라로는 풀 수 있있지만, MST로 푸는 방법을 몰라 질문하여 알았다. 경사도에 대해 이분탐색을 하여 조건을 만족한는 최대값중 최소값을 찾으면 되는 문제였다. 사실 MST로 풀려면 이차원 배열에 대해 DSU를 해야하는데 find, merge할 때 노드 번호를 y*n+x+1 이런식으로 해서 일차원 배열로 접근해야하는지 감이 안와 BFS로 풀었다. BFS로 풀때도, 메모리초과가 계속 났는데, BFS에서 dx[],dy[]에 대해 접근할때 visit을 해줘야 했다. pop하기 전에 visit을 했더니 같은 곳을 계속 방문하여 큐의 크기가 엄청나게 커지는 문제가 발생했다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <tuple>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
int arr[1000][1000];
int dx[]={0,0,1,-1};
int dy[]={1,-1,0,0};
bool visit[1000][1000];
bool bfs(int x){
queue<pair<int,int>>q;
memset(visit,false,sizeof(visit));
q.push({0,0});
visit[0][0]=true;
while(!q.empty()){
int cy = q.front().first;
int cx = q.front().second;
q.pop();
if(cy==n-1 && cx==n-1) return true;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int ny = cy+dy[i];
int nx = cx+dx[i];
if(ny<0 || ny>=n || nx<0 || nx>=n) continue;
int diff = arr[cy][cx]-arr[ny][nx];
if(abs(diff)>x||visit[ny][nx]) continue;
visit[ny][nx]=true;
q.push({ny,nx});
}
}
return false;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
int min_slope=1e9+1,max_slope=-1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
cin>>arr[i][j];
min_slope= min(min_slope,arr[i][j]);
max_slope= max(max_slope,arr[i][j]);
}
}
int lo = 0,hi= max_slope - min_slope;
int ans =-1;
while(lo<=hi){
int mid = (lo+hi)/2;
if(bfs(mid)){
ans = mid;
hi = mid-1;
}
else
lo = mid+1;
}
cout<<ans;
}