서로소 집합(Disjoint set union)
06 Aug 2021
CTP 알고리즘 동아리에서 여름방학 코딩테스트반에 참여하여 공부한 내용입니다.
아래 자료는 수업에서 사용한 내용입니다.
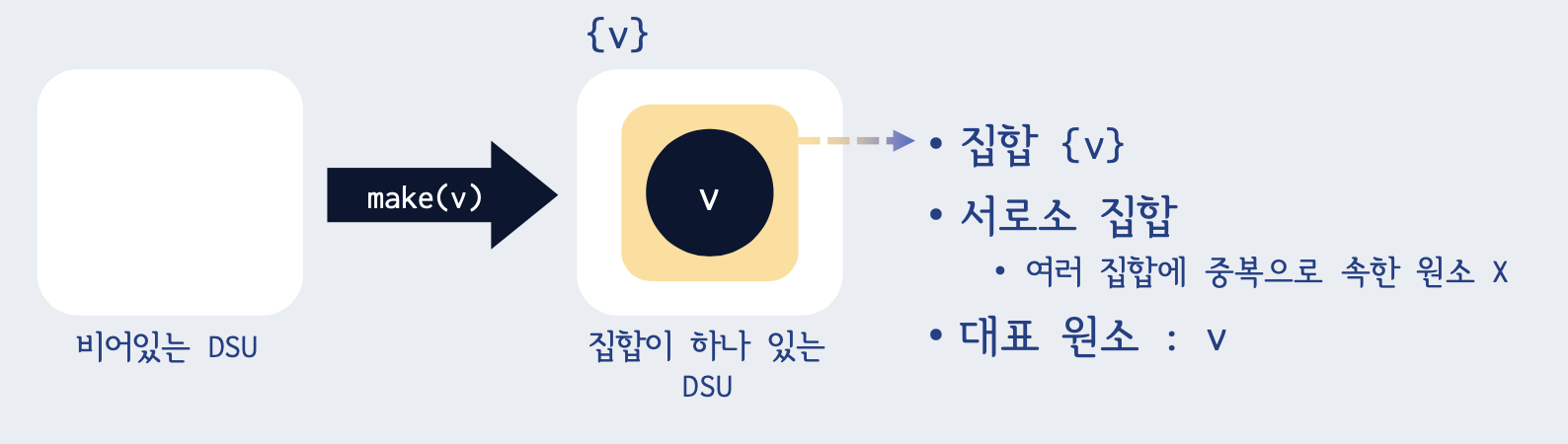
Disjoint set : 서로소 집합
- $set\;A\;\cap\;set\;B=\emptyset$ 을 만족하는 집합을 서로소 집합이라 하고, 서로소 집합으로 이루어진 자료구조를 의미한다. 개체를 집합의 원소로써 표현한다.
- 3가지 연산
-
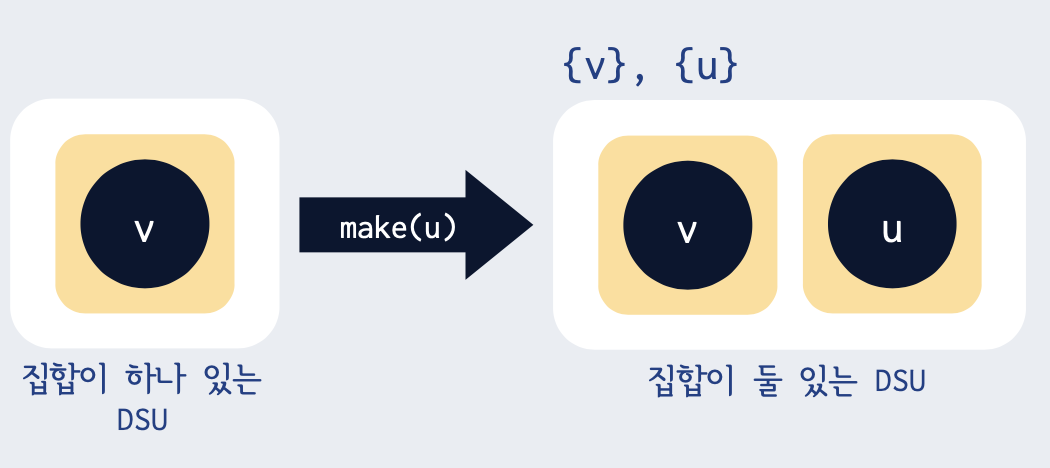
make(v) : 개체 v가 속해있는 집합 만들기
-
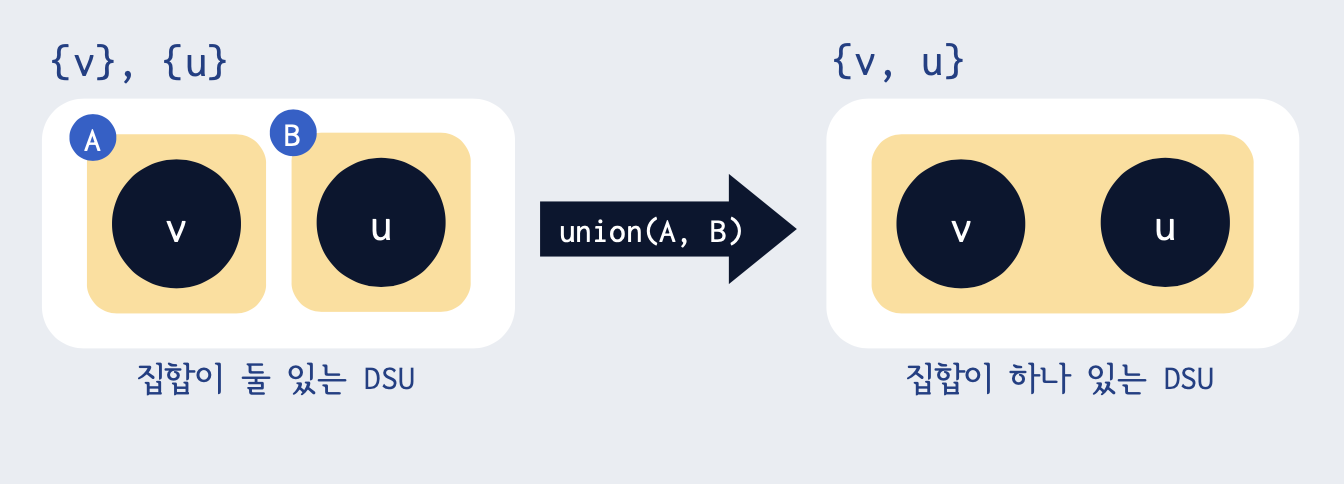
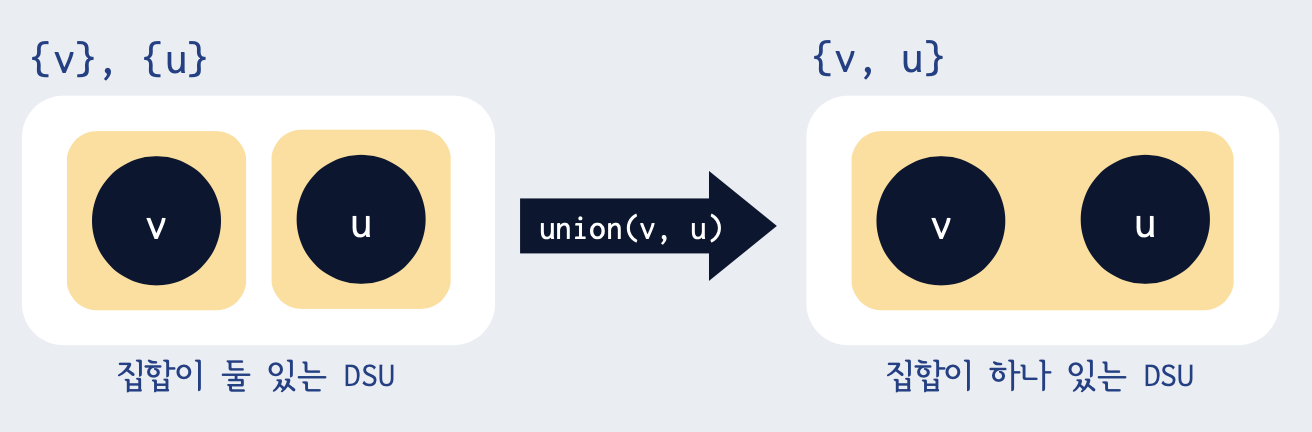
union(A, B) : 집합 A와 집합 B 합치기
또는 v가 속합 집합과 u가 속한 집합 합치기도 가능하다.
-
find(v) : 개체 v가 속한 집합의 대표 원소 찾기
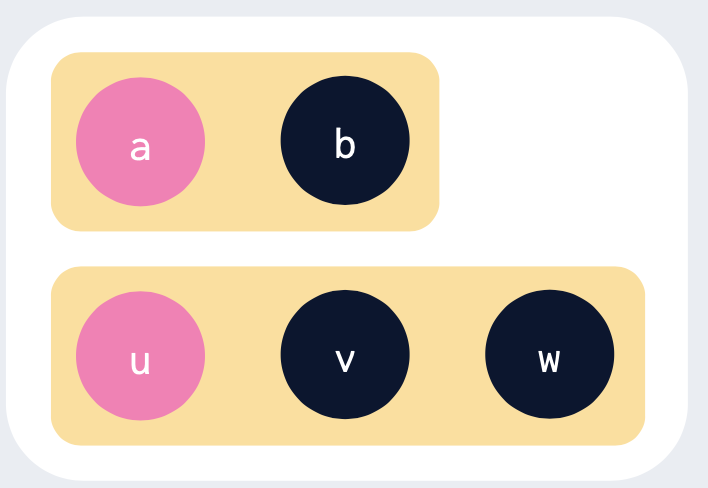
두 집합 {a,b}, {u, v, w} 에대해 각각 대표 원소가 a,u라고 가정.
- find(a),find(b) : 모두 a를 반환한다.
- find(u), find(v), find(w) : 모두 u를 반환한다.
→ make, union, find 모두 시간복잡도 O(1)에 매우 가깝게 할 수 있다.
-
DSU의 구현
- 트리 자료구조 기반
- 같은 집합이라도 여러가지 표현 방법이 존재한다.
- 어떤 원소가 루트노드인지는 중요하지 않다.
→ 필요한 것은 각 원소의 부모를 가리키는 간선 역할의 배열. (루트노드는 자기 자신을 가리키게 한다.)
-
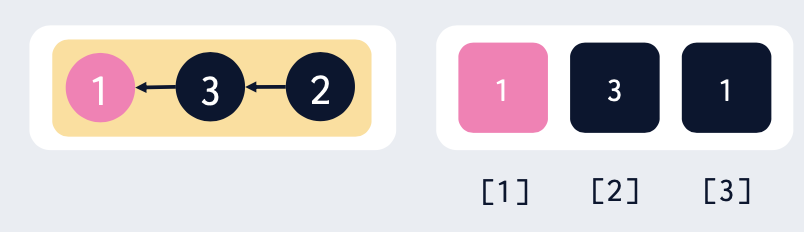
구현 : find
par[v] == v 라면, v가 집합의 대표 원소이므로, v를 반환한다. 아니라면 v의 부모노들를 타고 올라가다 보면 트리의 루트(대표원소)에 도달할 것이다.
int find(int v): if(par[v]==v) { return v;} else { return find(par[v]);} -
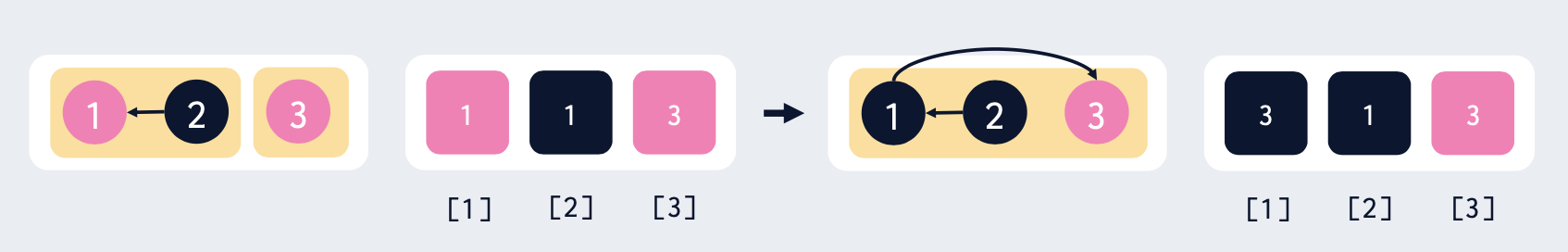
구현 : union
a가 속한 집합의 대표 원소를 a_root, b가 속한 집합의 대표원소를 b_root라 하자. a_root와 b_root가 서로 다르면, a와 b는 서로 다른 집합에 속한다. b_root에 해당하는 원소의 부모를 a_root에 해당하는 원소로 한다. 이제 b_root와 그의 모든 자식노드에 find 연산을 적용하면 a_root를 반환할 것이다.
void union(int a, int b): int a_root = find(a), b_root = find(b); if(a_root!=b_root) {par[b_root] = a_root;}
시간 복잡도 O(1)과 최적화 (경로 압축)
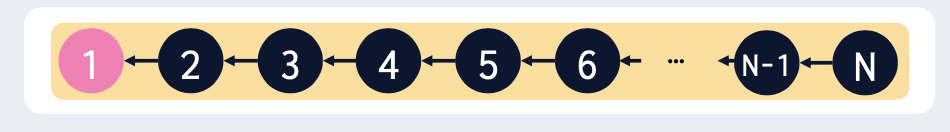
1부터 N까지의 원소가 N개의 집합에 하나씩 속해 있을때, union(1,2),union(2,3),..,union(N-1,N)을 적용하면 다음과 같은 트리가 된다.
이러한 트리 형태에서 find의 시간복잡도는 O(N)이다. → 최적화를 통해 O(1)로 만들어보자.
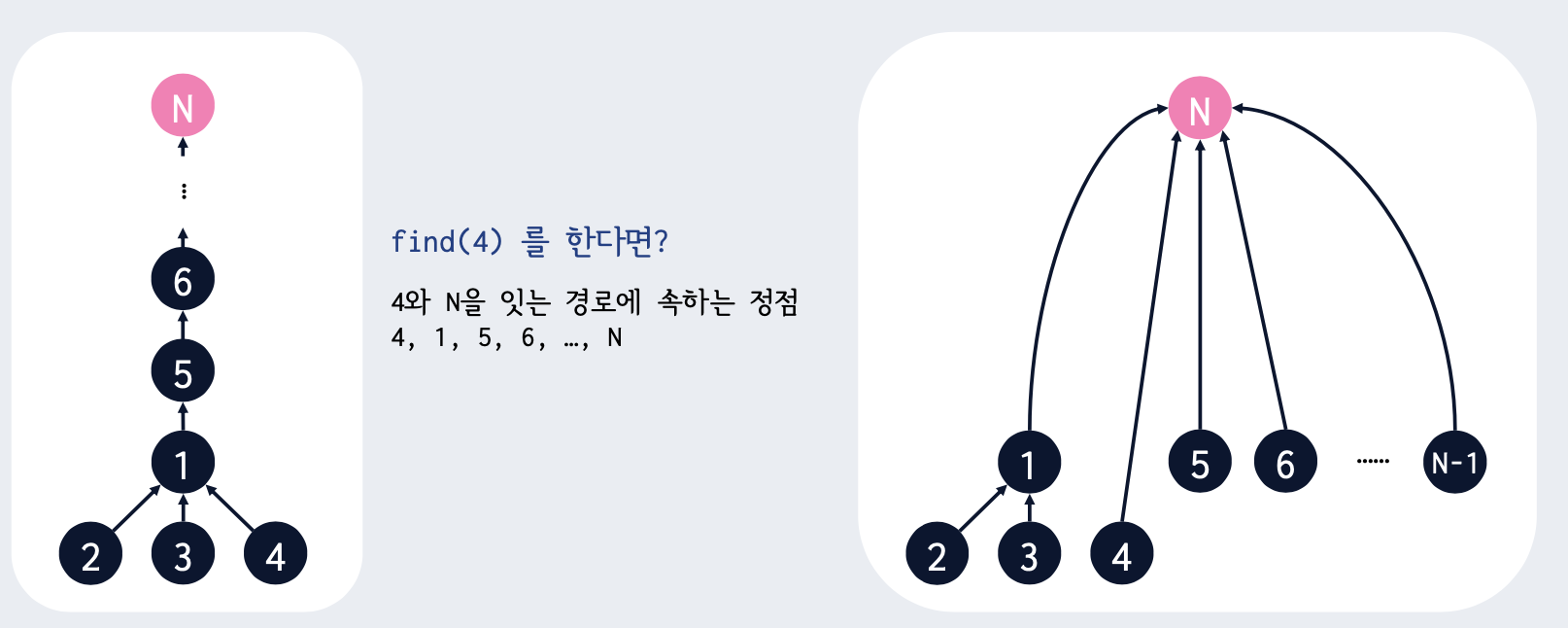
2~N번 원소에 대해 결과적으로 1번이 루트노드이다. 루트노드로 가는 경로에 있는 노드가 어떤 노드인지는 중요하지 않다.
int find(int v):
if(par[v]==v) return v;
else return par[v] = find(par[v]);
위와 같이 부모 노드를 대표노드로 바꾸어 저장하면, 정점 v와 대표 정점을 잇는 경로 상의 모든 정점의 부모가 대표정점로 바뀐다.
find 연산의 시간복잡도 : 많이 수행할수록 O(1)에 매우 가까워 진다. 실제 시간복잡도는 O( inverse Ackermannn function (n)) 이지만 다루지 않는다. 사실상 O(1)이라고 알고 넘어가도 좋다.
union연산은 개선의 여지가 있지만 다루지 않는다. ( Union by size와 관련되어 있다.)
A - 집합의 표현
초기에 {0}, {1}, {2}, … {n} 이 각각 n+1개의 집합을 이루고 있고, 여기에 합집합 연산과, 두 원소가 같은 집합에 포함되어 있는지를 확인하는 연산을 수행할때, 집합을 표현하는 프로그램을 작성하는 문제이다. DSU 구현과 동일한 문제였다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int n,m;
int par[1000001];
int find(int a){
if(par[a]==a) return a;
return par[a]=find(par[a]);
}
void merge(int a,int b){
int a_root = find(a),b_root=find(b);
if(a_root!=b_root) par[a_root]=b_root;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
par[i]=i;
}
for(int i=0,p1,p2,p3;i<m;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2>>p3;
if(p1==0){
merge(p2,p3);
}
if(p1==1){
if(find(p2)==find(p3))
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
B - 사이클 게임
DSU 문제로, 평면 상의 점이 같은 집합에 속하게 되면 사이클이 생긴다. merge(union) 하기 전에, 합치려는 노드가 부모의 노드인지 확인하면 된다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int n,m;
int par[500001];
int find(int a){
if(par[a]==a) return a;
return par[a]=find(par[a]);
}
void merge(int a,int b){
int a_root = find(a),b_root=find(b);
if(a_root!=b_root) par[b_root]=a_root;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
par[i]=i;
}
int ans=1000001;
for(int i=0,p1,p2;i<m;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2;
if(find(p1)==find(p2)){
ans = min(ans,i+1);
}
merge(p1,p2);
}
if(ans==1000001)
cout<<0<<endl;
else
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
C - Milk Visits
endpoint에 대한 노드 두개가 주어졌을때, 두개 노드의 경로를 모두 알아야할 필요는 없다. 두개의 노드 사이에 어떤 말의 종류가 있는지가 중요하다. 같은 종류의 소 일 경우 같은 집합으로 묶어준다. 인접된 노드의 부모가 다른 경우 H,G가 모두 있는 경우이고, 부모가 같다면 H인지 G인지 확인하면 된다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int n,m;
string str;
char cow[100001];
int par[100001];
int find(int a){
if(par[a]==a) return a;
return par[a]=find(par[a]);
}
void merge(int a, int b){
int a_root = find(a),b_root=find(b);
if(a_root!=b_root)par[b_root]=a_root;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m>>str;
memset(cow,0,sizeof(cow));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cow[i]=str[i-1];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
par[i]=i;
}
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
int p1,p2;
cin>>p1>>p2;
if(cow[p1]==cow[p2]){
merge(p1,p2);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int p1,p2;
char horse;
cin>>p1>>p2>>horse;
if(find(p1)!=find(p2)) cout<<1;
if(find(p1)==find(p2)){
if(cow[find(p1)]==horse)cout<<1;
else cout<<0;
}
}
return 0;
}