트리(Tree)
29 Jul 2021
CTP 알고리즘 동아리에서 여름방학 코딩테스트반에 참여하여 공부한 내용입니다.
아래 자료는 수업에서 사용한 내용입니다.
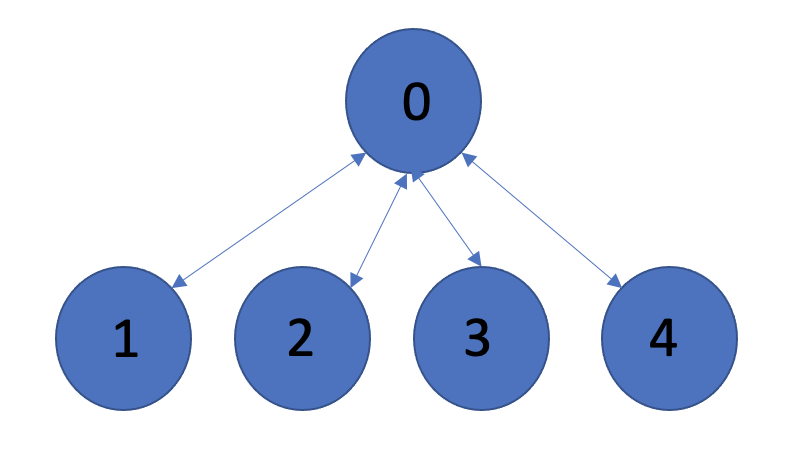
트리는 자료구조 그래프의 부분집합으로써, 특이한 성질이 있어 일반적인 그래프와 달리 할 수 있는 일이 많다.
트리의 조건
- 연결 그래프이다 임의의 서로 다른 두 정점을 잇는 경로가 존재한다.
- 사이클이 존재하지 않는다. ( 간선의 방향 무시) 앞서 언급한 경로는 어떤 두 정점에 대해 하나만 존재한다.
용어
- 깊이 : root에서 출발했을때 지나야하는 간선수
- 높이 : 최대 깊이 또는 1을 더하기도 함
- 부모-자식 : 인접한 두 노드에 대해 루트에 가까운 쪽이 부모
- 리프노드 : 자식이 없는 노드
- 서브트리 : 트리에 포함된 트리
트리의 성질
- 간선 개수는 반드시 노드 개수보다 1 적다
- 루트 노드를 제외한 모든 노드는 반드시 부모 노드를 하나 가진다.
- 트리의 아무 노드나 루트노드로 정해도 트리이다.
- 트리는 재귀적 구조를 가지고 있다. 트리는 서브트리를 포함하고, 서브트리 역시 트리이므로 서브트리를 포함한다.
트리 순회
- 전위 순회(preorder traversal) : 부모 방문 → 자식들 방문
- 후위 순회(postorder traversal) : 자식들 방문 → 부모 방문
이진트리
- 모든 노드에 대해 자식의 수가 최대 2인 트리
- 중위 순회(Inorder traversal)를 할 수 있다. 왼쪽 자식노드 방문 → 루트 노드 방문 → 오른쪽 자식 노드 방문
포화 이진트리
- 리프노드가 아닌 노드는 반드시 자식 노드를 둘 갖는다.
- 모든 리프 노드의 깊이가 같다.
- 높이가 h일때, 리프노드 : $2^h$개
- 노드 : $2^{h+1}-1$개
- 높이 : $O(log 노드수)$
트리의 재귀적 구조
- 재귀적인 그래프 탐색으로 구간 [L:R]의 구간합을 구할 수 있다. → DFS
- 높이가 $O(log N)$인 포화 이진 트리인 경우, O(log N)에 구간합을 구할 수 있다. 많아야 2*logN개의 노드 방문
트리에서의 다이나믹 프로그래밍
- Tree DP
- DP : 큰 문제를 부분 문제로 나누어 푸는 방법 전체 트리의 문제를 서브 트리의 해를 이용하여 풀 수 있다.
- 전위 순회와 후위 순회
- DFS를 이용한 순회
- 부모와 자식 중 어느 쪽을 먼저 방문하는지 여부가 다르다.
- 전위 순회
- 부모 노드의 해를 결정하여 자식노드에게 전달
-
트리의 높이 구하기
void dfs(int H) { ans = max(ans, H); for (각 자식노드) { dfs(H + 1) } } - 후위순회
- 서브 트리의 해를 이용해 전체 트리의 문제 해결
- 많은 트리 DP 문제에 해당
-
일반적인 구조
func dfs(int v) { for (sub_v : 자식노드들) { dfs(sub_v) dp[v] = dp[sub_v] 를 이용해 결정 } }
A - 트리의 부모 찾기
dfs로 탐색하여 1번 노드를 루트로 각 노드의 부모를 찾아주었다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
vector<vector<int>>v;
int n;
bool visit[100001];
int parent[100001];
void dfs(int x){
if(visit[x])
return;
visit[x]=true;
for(auto&i:v[x]){
if(visit[i])continue;
parent[i] = x;
dfs(i);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0,p1,p2;i<n-1;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2;
v[p1].push_back(p2);
v[p2].push_back(p1);
}
dfs(1);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
cout<<parent[i]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
B - 너구리 구구
dfs로 탐색하여 다음 코드로 문제를 풀었다. i.first = 자식 노드, i.second = 자식 노드까지의 cost
cost = max(cost,dfs(i.first)+i.second);
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,ll> pi;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int n;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
bool visit[5001];
ll dfs(int x){
if(visit[x])
return 0;
visit[x] = true;
ll cost =0;
for(auto& i:v[x]){
if(visit[i.first]) continue;
cost = max(cost,dfs(i.first)+i.second);
}
return cost;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0,p1,p2;i<n-1;i++){
ll c;
cin>>p1>>p2>>c;
v[p1].push_back({p2,c});
v[p2].push_back({p1,c});
}
cout<<dfs(1);
}
C - 인하니카 공화국
리프노드들의 cost합과 자신의 cost중 작은 것을 선택한다. 내가 구현한 코드에서 1번노드의 자식이 한개인 경우에 대해서 예외처리를 안해주어 계속 틀렸다. 다이나믹 프로그래밍이라 써있긴 하지만 dfs만 사용해도 풀렸다. dfs(v,i.first) → 리프노드들의 cost합, i.second = 자신의 cost를 의미한다.
cost += min(i.second,dfs(v,i.first));
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int t,n,m;
bool visit[1001];
int dp[1001];
int dfs(vector<vector<pi>>& v,int x){
if(dp[x]!=-1)
return dp[x];
visit[x] = true;
if(x!=1 && v[x].size()==1)
return dp[x]=v[x].front().second;
dp[x]=0;
for(auto&i:v[x]){
if(visit[i.first]) continue;
dp[x] += min(i.second,dfs(v,i.first));
}
return dp[x];
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>m;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
v.resize(n+1);
memset(visit,false,sizeof(visit));
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
for(int i=0,p1,p2,d;i<m;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2>>d;
v[p1].push_back({p2,d});
v[p2].push_back({p1,d});
}
dfs(v,1);
cout<<dp[1]<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
D - 트리 순회
전위,중위,후위 순회에 대한 문제였다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<int>> v;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int n;
void preorder(int x){
char tmp = x+'A';
cout<<tmp;
for(auto& i:v[x]){
if(i==('.'-'A'))continue;
preorder(i);
}
}
void postorder(int x){
char tmp = x+'A';
for(auto& i:v[x]){
if(i==('.'-'A'))continue;
postorder(i);
}
cout<<tmp;
}
void inorder(int x){
char tmp = x+'A';
char lc,rc;
if(v[x][0]!=('.'-'A')) {
inorder(v[x][0]);
}
cout<<tmp;
if(v[x][1]!=('.'-'A')) {
inorder(v[x][1]);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
char p1,lc,rc;
cin>>p1>>lc>>rc;
v[p1-'A'].push_back(lc-'A');
v[p1-'A'].push_back(rc-'A');
}
preorder(0);
cout<<endl;
inorder(0);
cout<<endl;
postorder(0);
}
E - 단절점과 단절선
처음에 시간복잡도를 생각하지 않고 dfs 탐색했다가 시간초과가 났다. 이렇게 하면 O(10^10)인 것을 확인하고 다른 방법을 생각했다. 정점의 차수가 1인것을 제외한 모든 정점이 단절점이 된다. 모든 간선은 단절선이다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
int n,q;
bool visit[100001];
int degree[100001];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1,p1,p2;i<n;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2;
degree[p1]+=1;
degree[p2]+=1;
}
cin>>q;
for(int i=0,t,k;i<q;i++){
cin>>t>>k;
if(t==1) {
if (degree[k] == 1)
cout << "no" << endl;
else
a cout << "yes" << endl;
}
else
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
F - 전단지 돌리기
케니소프트 위치 S를 root로한 트리에서 각 노드의 높이를 DFS를 이용하여 구하면 된다. 다음은 각 노드의 높이를 구하는 코드이다. 문제에서 주어진 힘이 어떤걸 의미하는 지 몰라서 한참 헤맸다. 전단지 던지는 힘이었다. ㅋㅋ
for(auto&i:v[x]){
if(visit[i])continue;
h[x]= max(dfs(i)+1,h[x]);
}
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<int>> v;
int n,s,d;
bool visit[100001];
int h[100001];
int dfs(int x){
visit[x]=true;
h[x] =0;
for(auto&i:v[x]){
if(visit[i])continue;
h[x]= max(dfs(i)+1,h[x]);
}
return h[x];
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>s>>d;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0,p1,p2;i<n-1;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2;
v[p1].push_back(p2);
v[p2].push_back(p1);
}
dfs(s);
int dist=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i!=s && h[i]>d-1){
dist+=1;
}
}
cout<<dist*2<<endl;
}
G - 회사 문화 1
한사람이 여러번 칭찬 받는 경우를 고려해야 한다. dfs를 이용하였고, 노드번호와 칭찬받는 정도를 함수 인자로 넘겨주었다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<int>> v;
ll tk[100001];
bool visit[100001];
ll hm[100001];// how much
void dfs(int x,ll k){
visit[x]=true;
hm[x]=k;
for(auto&i:v[x]){
if(visit[i])continue;
dfs(i,k+tk[i]);
}
}
int n,m;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1,p1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>p1;
if(p1!=-1) {
v[i].push_back(p1);
v[p1].push_back(i);
}
}
for(int i=0,p1,p2;i<m;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2;
tk[p1]+=p2;
}
dfs(1,tk[1]);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<hm[i]<<' ';
}
}
H - 버스노선
모든 도로에 적어도 하나 이상의 버스 노선이 지나가는 버스 노선의 최소 개수를 구하는 문제이다.
어떤 리프노드에서 다른 리프노드까지 도달하는 방법이라고 생각했다. 위와 같은 경우에 대해 1→0→2 /3/4으로 3가지가 나온다. 하지만 서로 다른 경로에서 출발점과 도착점이 아닌 경유 정류장은 겹칠 수 있으므로 1→0→2/3→0→4 : 2가지 이다.
dfs를 leaf 노드에서 시작하면 겹칠 수 있는 경우에 대해 고려할 수 없다. 그래서 dfs를 차수가 가장 높은 노드에서 시작하여 leaf 노드로 가는 경우의 수를 세준후, 2로 나누고 올림 하였다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<int>> v;
int n,root;
bool visit[200001];
int dfs(int x){
visit[x] = true;
int count = 0;
if(v[x].size()==1 && x!=root)
return 1;
for(auto&i:v[x]){
if(visit[i]) continue;
count+=dfs(i);
}
return count;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
v.resize(n);
for(int i=0,p1,p2;i<n-1;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2;
v[p1].push_back(p2);
v[p2].push_back(p1);
}
root = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(v[i].size()>v[root].size()){
root=i;
}
}
int ans = dfs(root);
if(ans%2==1)
cout<<(ans+1)/2;
else
cout<<ans/2;
}
I - 대기업 승범이네
못풀어서 해설을 참고했다. 홍익대 대회 자료 여기서 해설 읽고 구현하였다.
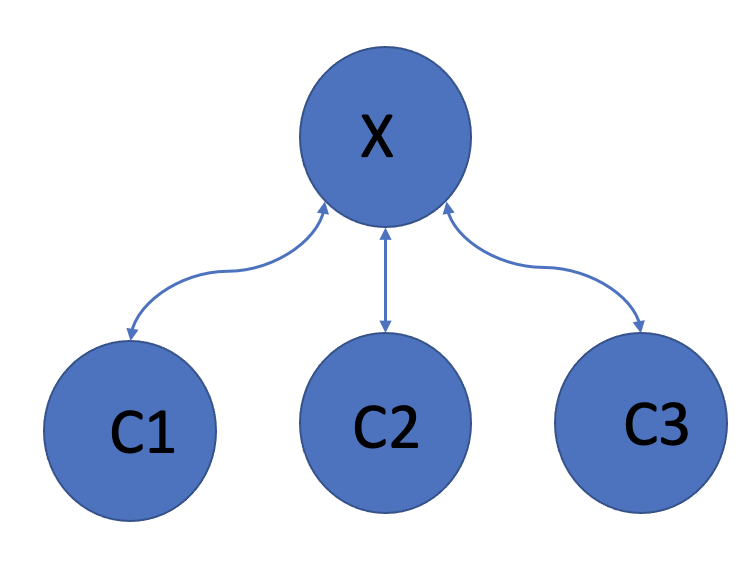
노드 x와 x의 서브트리가 있을때, 서브트리는 x가 멘토를 갖고있는 지만 관심이 있다. 즉, dp[x][hasMentor]를 사용하면 된다. (항상 dp 2차원배열이상으로 늘어나면 헤멘다..)
(1) dp[x][1] : x의 멘토가 있을 경우이다. 이때는 dp[x][1] = dp[c1][0]+dp[c2][0]+dp[c3][0]이 된다.
(2) dp[x][0] : x의 멘토가 없을 경우이다. 이때는 x-c1, x-c2, x-c3 가 사수-부수사인 경우를 (1)에 추가하여 고려해야 한다. dp[c1][0]~dp[c3][0]의 합을 미리 구해놓고 아래와 같이 구하면 된다. 미리 구한합에 dp[i][0]을 빼고, dp[i][1] + x능력 * i 능력 하면 된다.
(1) dp[x][1] = dp[x][1] = dp[c1][0]+dp[c2][0]+dp[c3][0];
(2) dp[x][0] = max(dp[x][0], no_mentor_su, - dp[i][0] +dp[i][1]+p[x]*p[i]);
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<vector<int>> v;
int n;
ll p[200001];
ll dp[200001][2];
bool visit[200001];
void dfs(int x){
visit[x]=true;
ll no_mentor=0;
for(auto i:v[x]){
if(visit[i])continue;
dfs(i);
}
for(auto i:v[x])
no_mentor+=dp[i][0];
dp[x][1]=no_mentor;
dp[x][0]=no_mentor;
for(auto i:v[x]) {
dp[x][0] = max(dp[x][0], no_mentor - dp[i][0] +dp[i][1]+p[x]*p[i]);
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=2,p1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>p1;
v[p1].push_back(i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>p[i];
}
ll ans =0;
dfs(1);
cout<<max(dp[1][0],dp[1][1]);
}