다익스트라 알고리즘(Dijkstra)
25 Jul 2021
CTP 알고리즘 동아리에서 여름방학 코딩테스트반에 참여하여 공부한 내용입니다.
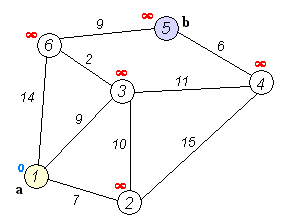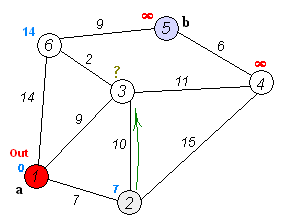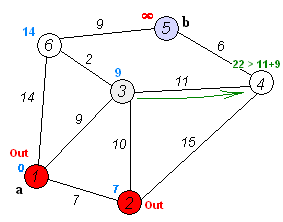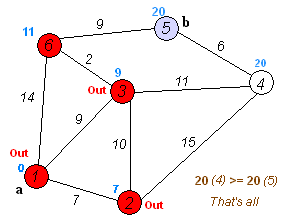
다익스트라 알고리즘이 하는 일은 그래프의 어떤 정점 하나를 시작점으로 선택하고 나머지 정점들로의 최단거리를 모두 구합니다. 무향,유향 그래프에 모두 사용할 수 있고, 거리(cost)값이 음수가 아닌 경우만 사용할 수 있습니다.
위의 무향 그래프에서의 작동을 예시로 들어 설명하겠습니다.
다익스트라 알고리즘은 다음과 같이 작동합니다.
- 아직 방문하지 않은 정점들 중 가장 짧은 정점을 하나 선택해 방문한다.
- 해당 정점에서 인접하고 아직 방문하지 않은 정점들의 거리를 갱신한다.
처음의 시작점으로의 거리만 0이고, 다른 거리들의 초기값은 무한입니다. 모든 정점에 대해 위의 (1),(2)이 작동하면 각 dist[i]는 1번 정점으로부터의 실제 최단 거리가 됩니다.
다익스트라 알고리즘에서 우선순위 큐 가 쓰이는 이유에 대해 설명해 보겠습니다. 아직 방문하지 않은 정점들 중에서dist 값이 제일 작은 정점을 찾아 방문하는 부분이 문제 입니다. 그냥 dist값들을 모두 비교하면 O(V^2)의 시간복잡도가 발생하므로, 여기서 우선순위 큐가 사용됩니다.
Min Heap을 하나 만듭니다. 정점 u를 방문해서 인접한 정점 v의 거리를 갱신할때 마다 최소 힙에 (dist[v],v) 쌍을 넣습니다. pair에 대해 대소 비교를 하면 첫번째 인자인 dist가 나와 가장 작은 dist가 우선순위 큐에서 나옵니다. dist값이 제일 작은 것을 뽑아서, 두번째 인자인 정점 번호를 사용하면 됩니다.
우선순위 큐에 남아있는 v 점점의 다른 pair에 대해서는 그냥 놔뒀다가 추후에 top에서 나타나면 무시합니다. 즉 꺼낸 정점이 이미 방문한 곳이면 무시하고 다음 top을 꺼내면 됩니다.
이렇게 하면 한 정점에서 최대한 많은 갱신이 이루어진다고 가정하여 V^2의 정보가 우선순위 큐에 있다고 해도, 우선순위 큐의 원래의 시간 복잡도가 O(logN)이므로, O(log(V^2)) = O(2logV)가 걸립니다.
즉, 루프 전체를 통틀어서 인접한 정점으로의 거리를 갱신하는 부분도 최대 O(E)번 이루어질것 이므로, 총 시간복잡도는 O(ElogV)입니다.
한가지 예외처리 해야할 것은 그래프 자체가 연결 그래프가 아니거나, 유향그래프일 때 시작점에서 어떤 정점으로 못갈 때는 루프를 꼭 V-1번 돌지 못합니다. 중간에 우선순위 큐가 비어버리고, 아직 방문하지 못한 점점들의 경우에는 거리가 무한으로 남아 있게된다. (시작점에서 그 정점으로 갈 수 없다.)
Priority Queue STL 사용법
우선순위 큐는 priority_queue<자료형, 구현체, 비교 연산자>로 정의 한다.
자료형은 int,double, 선언한 클래스 등을 의미한다.
구현체는 기본적으로 vector<자료형>으로 정의 된다. 우리가 쓰는 priority_queue는 vector 위에서 작동하고, vector가 아니어도 STL에서 heap을 구현하기 위한 자료구조면 모두 작동한다.
비교 연산자는 기본적으로 less<자료형>으로 정의된다. STL에서 기본으로 제공하는 비교 연산자 클래스로, 내림차순이 된다. greater<자료형>을 비교 연산자로 입력하면 오름차순이된다.
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int> > q;
int main(){
q.push(3);
q.push(1);
q.push(4);
q.push(1);
q.push(5);
q.push(9);
while (!q.empty()) {
cout<<q.top()<<' ';
q.pop();
}
}
// 출력 : 9 5 4 3 1 1
문제를 풀다 궁금해진 점이 아래의 상황에서는 첫번째인자가 같을때 어떻게 동작하는지 궁금했다.
typedef pair<int,pair<int,int>> pii;
priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii>> q;
출력해보니, (first, second.first, second.second 순으로) 값이 같은 경우 다음 인자를 비교하는 방식으로 동작했다.
A - 최단경로
방향그래프의 정점, 간선 수, 시작 정점을 순서대로 입력 받고 시작점을 기준으로 다익스트라 알고리즘을 실행시켜 시작점에서 각 정점까지의 거리를 출력한다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> P;
int dist[20001];
bool visit[20001];
vector<vector<P>> v;
priority_queue<P,vector<P>,greater<P>> q;
int a,e,k;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>a>>e>>k;
v.resize(a+1);
for(int i=0;i<e; i++){
int p1,p2,p3;
cin>>p1>>p2>>p3;
v[p1].push_back({p2,p3});
}
fill(dist+1,dist+1+a,INF); // 정점 V가 1부터 시작하므로 dist+1
dist[k]=0;
q.push({0,k}); // 시작점
while(!q.empty()){
int cur;
do{
cur = q.top().second; // PQ의 첫번째 인자는 거리, 두번째 인자는 정점
q.pop();
}while(!q.empty()&&visit[cur]);
if(visit[cur]) // 방문했다면 break;
break;
visit[cur] = true;
for(auto i : v[cur]){
if(dist[i.first]>dist[cur]+i.second){
dist[i.first] = dist[cur]+i.second;
q.push({dist[i.first],i.first});
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=a;i++){
if(dist[i]==INF)
cout<<"INF"<<endl;
else{
cout << dist[i] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
B - 배열 탈출
n x n 2차원 배열의 {0,0}에서 출발하여 {n-1,n-1}까지 도착하는데 최소 비용을 구하는 문제이다. 오른쪽 아래, 왼쪽 아래로만 이동 가능하며, 이동할 칸 보다 숫자가 커야 이동할 수 있다. 이동할 칸(ny,nx)가 더 크거나 같으면 버튼(=cost)을 눌러 dist[ny][nx] - dist[y][x] +1 만큼의 cost가 든다.
A번과 다른점이라면, 이차원에 대해 다익스트라를 적용해야 하므로 pair<int,pair<int,int»를 사용해야 한다. 첫번째 인자는 distance, 두번째 인자는 {y,x} 좌표이다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
typedef pair<int,pair<int,int>>pii;
int n;
int dist[3000][3000];
int mp[3000][3000];
bool visit[3000][3000];
int dx[]={0,1}; // 오른쪽/왼쪽 아래로만 이동함.
int dy[]={1,0};
vector<vector<pii>> v;
priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii>> q;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
cin>>mp[i][j];
dist[i][j] = INF;
}
dist[0][0] = 0;
q.push({0,{0,0}});
while(!q.empty()){
int y,x;
do{
y = q.top().second.first;
x = q.top().second.second;
q.pop();
}while(!q.empty()&&visit[y][x]);
if(visit[y][x])
break;
visit[y][x] = true;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
int ny,nx,ndist=0;
ny = y +dy[i];
nx = x + dx[i];
if(ny<0 || nx<0 || ny>=n || nx>=n) continue;
if(mp[ny][nx]>=mp[y][x]) ndist = mp[ny][nx]-mp[y][x]+1;
if(dist[ny][nx] > dist[y][x]+ndist){
dist[ny][nx] = dist[y][x] + ndist;
q.push({dist[ny][nx],{ny,nx}});
}
}
}
cout<<dist[n-1][n-1]<<'\n';
return 0;
}
C - 연애인은 힘들어
먼저, (1) 성하가 출발점일때 (2) 지헌이가 출발점일때 에 대한 각 정점들의 최단거리를 각각 구한다. 그 다음 지헌이와 성하의 정점을 제외해 (1번조건) 정점들에 대해 (1)의 최단거리와 (2)의 최단거리의 합의 최소를 구한다.(2번 조건) 그 최소를 만족하는 정점들 중 지헌이가 더 작거나 같은 정점 들에 대해 vector<int>ans에 넣어준다 (3번조건). 마지막으로 ans를 sort하여 가장 작은 정점을 출력한다.(4번 조건)
무향 그래프이기 때문에 양쪽다 입력을 넣어줘야 한다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
int dist[101]; // J 지헌 기준
int dist1[101]; // S 성하 기준
bool visit[101];
vector<vector<pi>> v;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int V,M,J,S;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>V>>M;
v.resize(V+1);
for(int i=0,p1,p2,p3;i<M;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2>>p3;
v[p1].push_back({p2,p3});
v[p2].push_back({p1,p3});
}
cin>>J>>S;
fill(dist+1,dist+1+V,INF);
fill(dist1+1,dist1+1+V,INF);
dist[J]=0;
q.push({0,J});
while(!q.empty()){
int cur;
do{
cur = q.top().second;
q.pop();
}while(!q.empty()&&visit[cur]);
if(visit[cur])
break;
visit[cur]=true;
for(auto&i:v[cur]){
if(dist[i.first]>dist[cur]+i.second){
dist[i.first] = dist[cur]+i.second;
q.push({dist[i.first],i.first});
}
}
}
memset(visit,false,sizeof(visit));
dist1[S]=0;
q.push({0,S});
while(!q.empty()) {
int cur;
do {
cur = q.top().second;
q.pop();
} while (!q.empty() && visit[cur]);
if (visit[cur])
break;
visit[cur] = true;
for (auto &i:v[cur]) {
if (dist1[i.first] > dist1[cur] + i.second) {
dist1[i.first] = dist1[cur] + i.second;
q.push({dist1[i.first], i.first});
}
}
}
int distMin = INF;
for(int i=1;i<=V;i++){
if(i ==J || i==S) continue;
distMin = min(distMin,dist[i]+dist1[i]);
}
vector<int>ans;
int JMIN = INF;
for(int i=1;i<=V;i++){
if(i ==J || i==S) continue;
if(distMin==dist[i]+dist1[i] && dist[i]<=dist1[i]) {
JMIN = min(JMIN,dist[i]);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=V;i++){
if(i ==J || i==S) continue;
if(distMin==dist[i]+dist1[i] && dist[i]<=dist1[i] && dist[i]==JMIN) {
ans.push_back(i);
}
}
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end());
if(ans.empty())
cout<<-1<<endl;
else
cout<<ans.front()<<endl;
return 0;
}
D - 도로포장
처음에는 N개의 도시중에 k개를 골라 도로를 포장하는 방법을 생각했는데, 조합의 시간복잡도 이므로 O(2^n)이었다. 그래서 dist[i][j] : i번째 도시에서 포장한 도로가 j개 일때로 dp를 사용하여 풀었다. visit[i][j]도 이차원 배열로 만들어주어야 한다. 위와 같이 해도 되는 이유는 n≤ 10,000, k≤20 이므로, 2*10^5이라 충분하다.
구현은 빨리 했으나, longlong을 고려하지 않아서 오래 걸렸다. INF 값도 int에서의 10^9으로는 부족했다. 최대 도로 길이가 10^10이다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pl;
typedef pair<ll,pair<ll,ll>> pll;
vector<vector<pll>> v;
priority_queue<pll,vector<pll>,greater<pll>> q;
ll dist[10001][21];
bool visit[10001][21];
int n,m,k;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m>>k;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0,p1,p2,p3;i<m;i++){
cin>>p1>>p2>>p3;
v[p1].push_back({p3,{p2,0}});
v[p2].push_back({p3,{p1,0}});
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=k;j++){
if(i==1)
dist[i][j]=0;
else
dist[i][j]=LINF;
}
q.push({dist[1][0],{1,0}});
while(!q.empty()) {
int cur;
int curk;
do {
cur = q.top().second.first;
curk = q.top().second.second;
q.pop();
} while (!q.empty()&&visit[cur][curk]);
if(visit[cur][curk])
break;
visit[cur][curk]=true;
for (auto&j:v[cur]) {
int nextk = curk + 1; // 다음 k번째 포장 도로.
if (dist[j.second.first][curk] > dist[cur][curk] + j.first) { // 포장하지 않은 경우
dist[j.second.first][curk] = dist[cur][curk] + j.first;
q.push({dist[j.second.first][curk], {j.second.first, curk}});
}
if (nextk <= k && dist[j.second.first][nextk] > dist[cur][curk]) { // 포장할 경우
dist[j.second.first][nextk] = dist[cur][curk];
q.push({dist[j.second.first][nextk], {j.second.first, nextk}});
}
}
}
ll ans = LINF;
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++)
if(ans>dist[n][i])
ans = dist[n][i];
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
E - 네트워크 복구
다익스트라를 이용하여 최단거리의 경로를 저장하면 된다. 최단거리가 같은 경로가 여러 개인 경우를 따로 고려하니 문제가 안풀렸다. 최단거리의 값이 갱신되는 부분에서 그 정점의 부모 정점을 갱신하면 해결되었다.
복구할 간선의 개수는 N-1개이다. 생각해보면 N개의 정점을 모두 연결하기 위해서는 최소 N-1개의 간선이 필요하다.
code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#define endl '\n'
#define INF 1e9
#define LINF 2e15
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
typedef pair<int,pair<int,int>> pii;
vector<vector<pi>> v;
priority_queue<pi,vector<pi>,greater<pi>> q;
int n,m;
bool visit[1001];
int dist[1001];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cin>>n>>m;
v.resize(n+1);
for(int i=0,a,b,c;i<m;i++){
cin>>a>>b>>c;
v[a].push_back({b,c});
v[b].push_back({a,c});
}
fill(dist+1,dist+1+n,INF);
dist[1]=0;
q.push({dist[1],1});
int parent[1001];
while(!q.empty()){
int cur;
do{
cur = q.top().second;
q.pop();
}while(!q.empty()&&visit[cur]);
if(visit[cur])
break;
visit[cur]=true;
for(auto&i : v[cur]){
if(dist[i.first]>dist[cur]+i.second){
dist[i.first] = dist[cur] + i.second;
parent[i.first]=cur;
q.push({dist[i.first],i.first});
}
}
}
cout<<n-1<<endl;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
cout<<parent[i]<<' '<<i<<endl;
return 0;
}
reference
(1) dijkstra algorithm (2) stl priority queue